FIGURE 5.
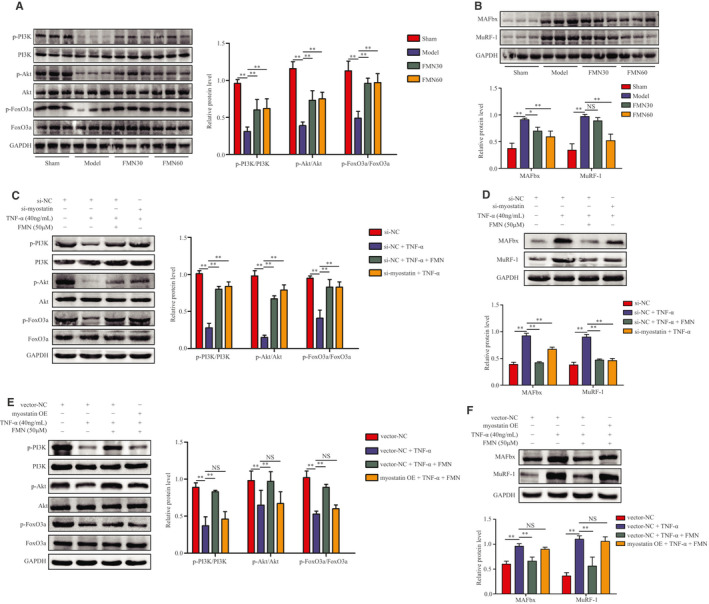
FMN inhibits myostatin‐mediated dephosphorylation on the PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signalling pathway in the muscle of CKD rats and C2C12 myotubes. (A) Protein levels of p‐PI3K, PI3K, p‐Akt, Akt, p‐FoxO3a and FoxO3a in gastrocnemius muscle analysed using Western blotting (n = 3/group). (B) Protein levels of MAFbx and MuRF‐1 in gastrocnemius muscles analysed using Western blotting (n = 3/group). (C) C2C12 myotubes were treated with FMN (50 μmol/L) in the presence or absence of TNF‐α (40 ng/mL) for 48 h following 24 h of incubation with si‐myostatin or si‐NC. The myotubes were divided into four groups: si‐NC, si‐NC + TNF‐α, si‐NC + TNF‐α + FMN (50 μmol/L) and si‐myostatin + TNF‐α. Protein levels of p‐PI3K, PI3K, p‐Akt, Akt, p‐FoxO3a and FoxO3a in C2C12 myotubes (n = 3/group). (D) Protein levels of MAFbx and MuRF‐1 in C2C12 myotubes (n = 3/group). (E) Myostatin OE transfection was used to overexpress myostatin in C2C12 myotubes, and they were incubated with FMN (50 μmol/L) and TNF‐α for another 48 h. The myotubes were divided into four groups: vector NC, vector NC + TNF‐α, vector NC + TNF‐α + FMN (50 μmol/L) and myostatin OE + TNF‐α + FMN (50 μmol/L). The protein levels of p‐PI3K, PI3K, p‐Akt, Akt, p‐FoxO3a and FoxO3a in the myotubes were analysed using Western blotting. (F) Protein levels of MAFbx and MuRF1 in C2C12 myotubes analysed by Western blotting (n = 3/group). *P < .05, **P < .01
