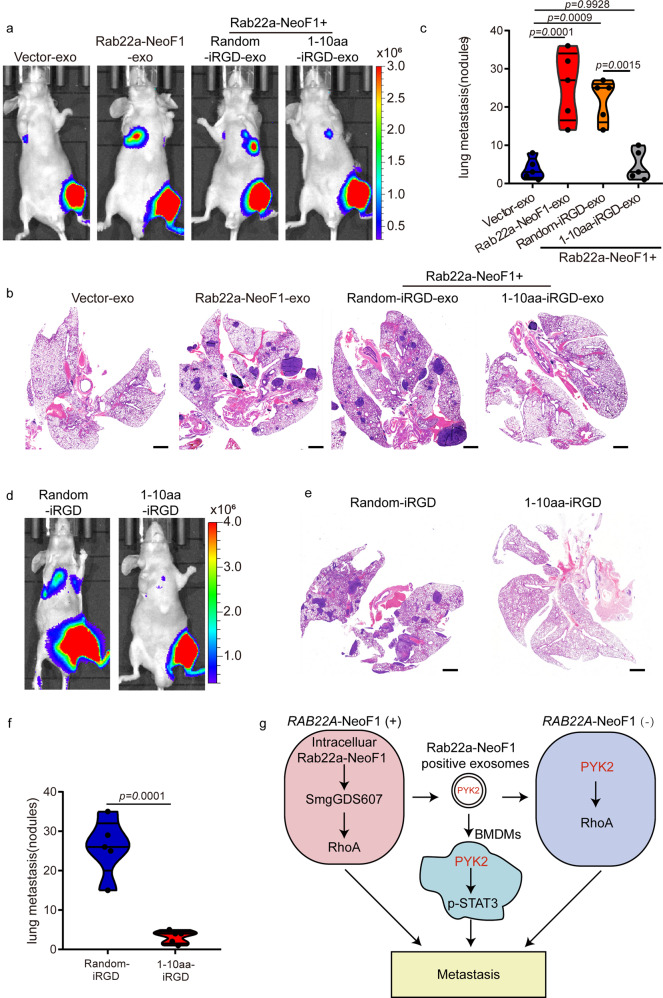
Fig. 8.
Blockage of the interaction between Rab22a-NeoF1 and PYK2 inhibits lung metastases of the recipient cells induced by the exosomal Rab22a-NeoF1 fusion protein. a–c Representative IVIS imaging (a), H&E-stained lung sections (b), and quantification of lung metastatic foci (c) from mice orthotopically injected 143B-Luc cells, and then were treated with the indicated exosomes. n = 5 biologically independent mice. Data are mean ± s.d. P values are shown. Scale bar, 2 mm. d–f Representative IVIS imaging (d), H&E-stained lung sections (e), and quantification of lung metastatic foci (f) from mice orthotopically co-injected U2OS/MTX300-Luc cells with ZOS-M cells at the 10:1 ratio under the treatment of either 1–10 a.a.-iRGD or random-iRGD peptide. n = 5 biologically independent mice. Data are mean ± s.d. P values are shown. Scale bar, 2 mm. g The proposed model for function and mechanism of Rab22a-NeoF1 fusion protein in osteosarcoma. A small proportion of tumor cells positive for Rab22a-NeoF1 fusion protein promote lung metastasis at least by three ways, Rab22a-NeoF1 fusion protein activates the cellular RhoA by constitutively binding to SmgGDS607; the exosomal Rab22a-NeoF1 fusion protein promotes RhoA activation in its negative recipient cancer cells by the exosomal PYK2 from donor cells, as well as facilitates the pre-metastatic niche formation in the lung by promoting BMDMs recruitment and by increasing M2 macrophages via the exosomal PYK2-mediated Stat3 activation from donor cells