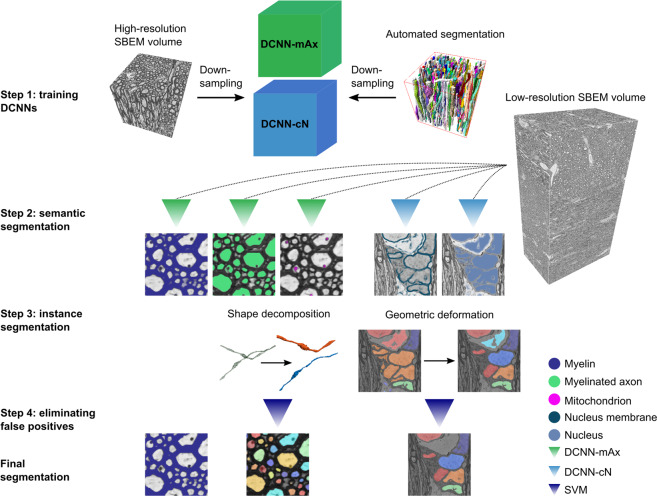
Fig. 1. DeepACSON pipeline.
Step 1: We used the ACSON segmentation of the high-resolution (small field-of-view) SBEM images down-sampled to the resolution of the low-resolution (large field-of-view) images to train DeepACSON. We trained two DCNNs denoted as DCNN-mAx and DCNN-cN. Step 2: DCNN-mAx returned the probability maps of myelin, myelinated axons, and mitochondria. DCNN-cN returned the probability maps of cell nuclei and the membrane of cell nuclei. Step 3: The segmentation of myelin was finalized by thresholding the myelin probability map. We performed the initial segmentation of myelinated axons by the binarization and connected component analysis. The geometry of the segmented components was subsequently rectified using our newly developed cylindrical shape decomposition (CSD) technique14. We performed the segmentation of cell nuclei in a geometric deformable model (GDM) framework by applying elastic deformations to the initial segmentation of cell nuclei. Step 4: The segmentation of myelinated axons and cell nuclei was finalized by eliminating non-axonal and non-nucleus structures using support vector machines (SVMs).