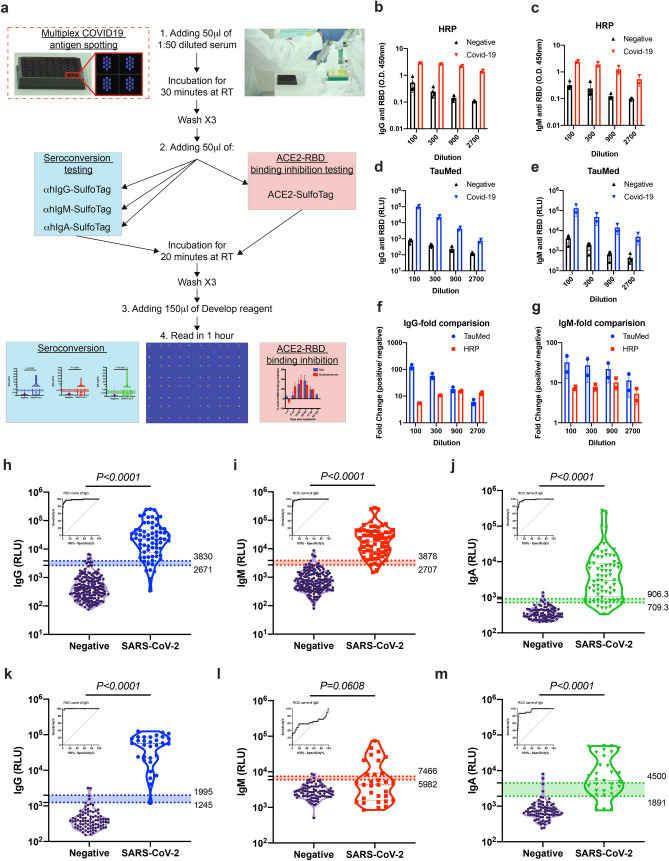
Figure 1.
Validation of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies using electrochemiluminescence ELISA. (a) Schematic illustration of our new developed serological test. (b–g) Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 HRP-based ELISA to electrochemiluminescence-based ELISA. The presence of anti-RBD IgG and IgM antibodies was determined in a side-by-side comparison using HRP-based ELISA (HRP) (b,c) and electrochemiluminescence-based ELISA (TauMed) (d,e). The fold changes in the values obtained from individual positive samples (n = 4) over the average negative samples (n = 2) were calculated (f,g). (h–m) Validation of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies using electrochemiluminescence ELISA. Peripheral blood was collected from the peripheral blood of > 14 DPS of hospitalized COVID-19 patients and anonymous recovered patients (n = 68 and n = 31 for RBD and NP respectively). Negative samples were obtained from true SARS-CoV-2 negative patients (i.e., prior to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic) (n = 197 and n = 90 for RBD and NP respectively). Plasma was obtained, diluted 1:50, and added to a 96-well plate precoated with SARS-CoV-2 RBD (h–j) or NP (k–m) antigens. IgG (h,k), IgM (i,l), and IgA (j,m) levels as well as ROC analysis are shown. Data were calculated using GraphPad Prism 8; the dotted line represents the calculated cutoff value discriminating between positive and negative samples. A nonparametric Mann–Whitney t-test was performed. P values are shown.