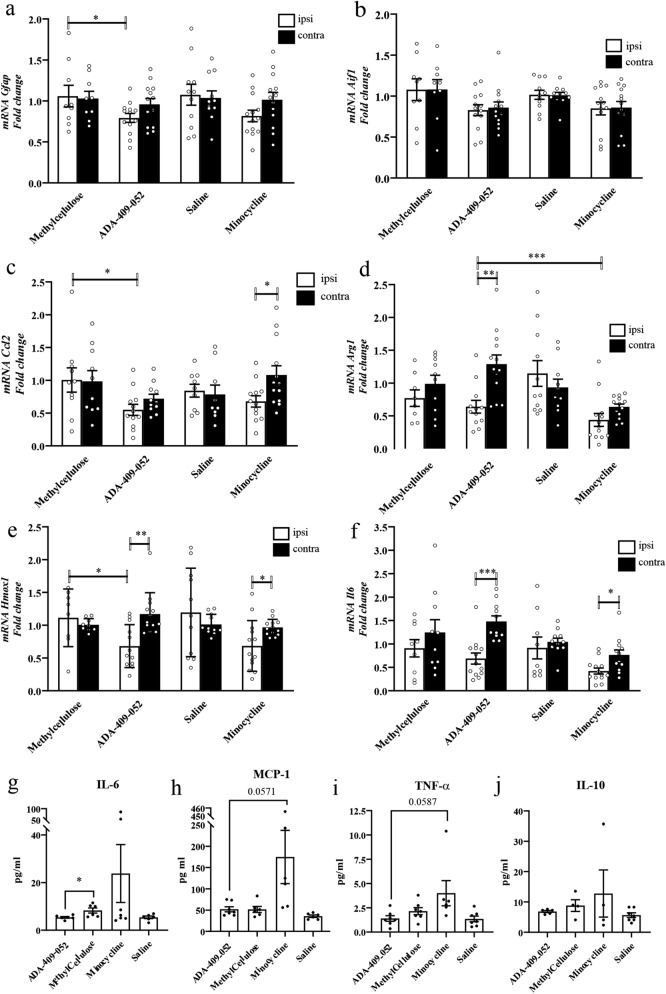
Figure 6.
ADA-409-052 administration in vivo reduced the expression levels of pro-inflammatory markers (a–f) and altered the peripheral cytokine secretion (g–j) at 1 day post-ischemia. The mRNA expression of tissue samples from the ipsi- and contralateral peri-ischemic area at 24 h was analyzed using qPCR. Expression levels of (a) Gfap and (c) Ccl2 were markedly reduced in the ipsilateral peri-ischemic area after ADA-409-052 treatment when compared to vehicle. (b) While, Aif1 remained unchanged throughout all groups, ADA-409-052 lowered (d) Arg1 and (e) Il6 mRNA expression in the ipsilateral samples when compared to contralateral. (f) Ischemic mice treated with ADA-409-052 showed reduced Hmox1 expression in the ipsilateral peri-ischemic area when compared to contralateral expression levels, to ipsilateral expression of vehicle-treated mice respectively. Minocycline decreased the expression of Hmox1 only ipsilateral when compared to contralateral. mRNA expression levels of peri-ischemic tissue samples from ipsi- and contralateral, data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m.; unpaired, two-tailed student’s t-test; n = 9–13; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.001. (g) The secretion of the inflammation-mediating IL-6 was significantly reduced in ADA-409-052-treated mice when compared to vehicle-treated mice, as detected from the blood plasma, collected from ischemic mice at 1 dpi, by using the BD CBA mouse inflammation kit. (h,i) Both MCP-1 and TNF-α were equally low in ADA-409-052-treated mice when compared with vehicle treatment and showed a clear trend towards reduction when compared with minocycline-treated mice (changes did not reach significance). (j) The peripheral secretion of IL-10 remained unaltered by any given treatment. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m.; unpaired, two-tailed student’s t-test; n = 7; *p = 0.027.