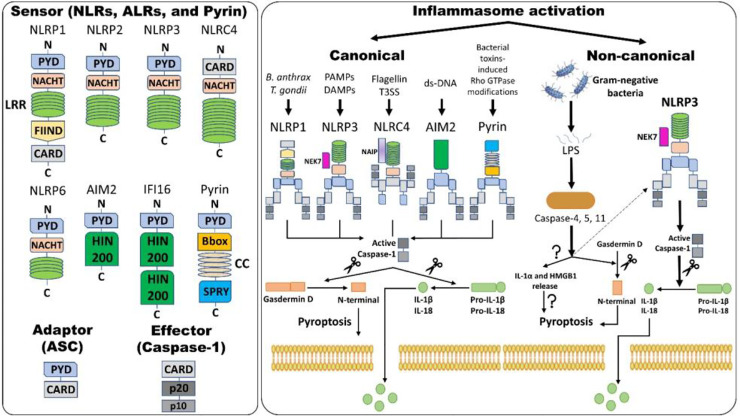
Figure 1.
Inflammasome assembly and activation pathways. An inflammasome consists of three proteins: sensor, adaptor, and effector. Please note that NLRP3 and NLRC4 require NIMA (Never in Mitosis Gene A)-related Kinase 7 (NEK7) and NLR family apoptosis inhibitory protein (NAIP), respectively, for activation. Canonical inflammasome activation results in the formation of active caspase-1 (activation) by removing caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD; processing). Active caspase-1 cleaves gasdermin D (GSDMD) and pro-interleukins into the N-terminal of GSDMD and mature interleukins, respectively. The N-terminal of GSDMD forms pores within the cell membrane, allowing mature IL-1β and IL-18 release along with changes in ion fluxes. Such caspase-1-dependent formation of plasma membrane pores releasing inflammatory intracellular materials resulting in cell lysis is termed pyroptosis. Alternatively, in non-canonical inflammasome activation, gram-negative bacteria release lipopolysaccharides (LPS) that activate caspase-4 and -5 in humans and caspase-11 in mice, which results in pyroptosis via several mechanisms. Firstly, GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis occurs as explained above and, secondly, activation of caspases leads to the release of IL-1α and high-mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) via unknown mechanisms, which results in pyroptosis. Caspase-4, -5, and -11 activation by LPS also indirectly activates the NLRP3 inflammasome, culminating in the maturation of IL-1β and IL-18 via activating caspase-1. Abbreviations: Nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) and leucine-rich-repeat-(LRR)-containing receptors (NLRs); Absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2)-like receptors (ALRs); pyrin domain (PYD); Caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD); Nucleotide-binding and oligomerization or NAIP, CIITA, HET-E and TP1 (NACHT) domain; Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing CARD (ASC); Interferon-gamma inducible protein 16 (IFI-16); Function-to-find domain (FIIND); Coiled-coil (CC); Bacterial type III secretion system (T3SS); Hematopoietic interferon-inducible nuclear protein with 200 amino acids (HIN-200).