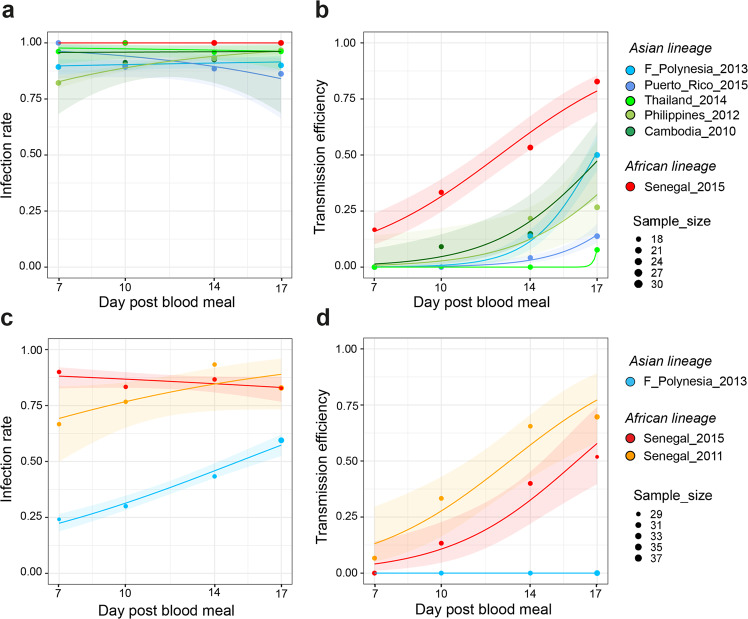
Fig. 2. Mosquito infection rate and transmission efficiency of African and Asian ZIKV strains.
Wild-type Ae. aegypti mosquitoes from Colombia were orally exposed to ZIKV and collected on day 7, 10, 14, and 17 post infectious blood meal to analyze their carcasses and saliva samples collected in vitro. Infection rates and transmission efficiencies over time are shown for each ZIKV strain tested after oral exposure to a high dose (5.6–5.8 log10 FFU/ml) (a, b) or a low dose (4.7–4.8 log10 FFU/ml) (c, d) of virus. Infection rate is the proportion of ZIKV-positive carcasses among all blood-fed mosquitoes (determined by RT-PCR). Transmission efficiency is the proportion of blood-fed mosquitoes with infectious saliva (determined by FFA). The data points represent the empirically measured proportions, and their size is proportional to the sample size (high dose: n = 18–30 mosquitoes per group; low dose: n = 29–37 mosquitoes per group). The lines represent the logistic regression results and the shaded areas are the 95% confidence intervals of the logistic fits. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.