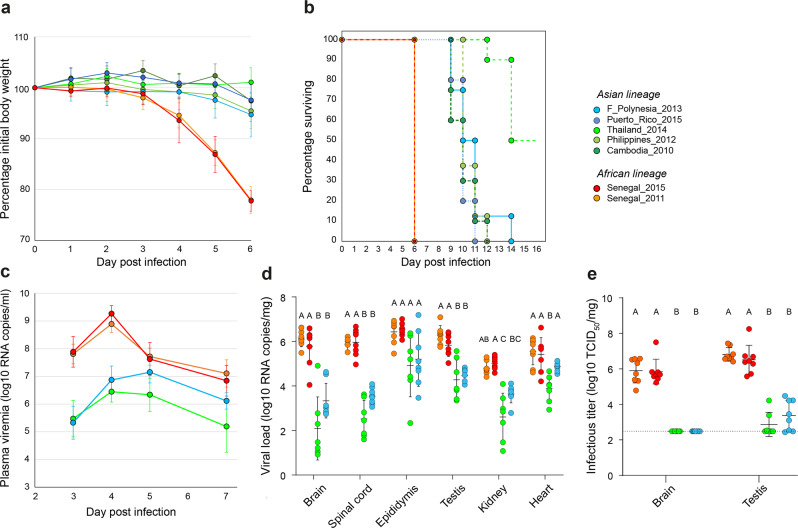
Fig. 4. Pathogenicity of African and Asian ZIKV strains in immunocompromised adult mice.
In a first experiment (a, b), male AG129 mice were inoculated with 103 PFU of ZIKV. Each virus strain was represented by n = 10 mice, with the exception of the F_Polynesia_2013 and Philippines_2012 strains that were represented by n = 8 mice. a Mouse weight over time is shown as the percentage of body weight prior to infection (mean ± standard error). b Mouse survival over time is shown as the percentage of mice alive. Mice were euthanized when reaching humane endpoints (weight loss >20% or/and severe symptom onset). In a second experiment (c–e), male AG129 mice were inoculated with 1 PFU of ZIKV (n = 8 mice per strain). c Time course of mouse viremia is shown in log10-transformed viral genome copies per ml of plasma (mean ± standard error). Three extreme outliers were excluded for the Senegal_2015 strain. d Viral loads in organs collected on day 7 post infection are shown in log10-transformed viral genome copies per mg of tissue. Statistical significance of differences was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for brain, heart and testis, by Brown–Forsythe and Welch ANOVA followed by Games-Howell’s post hoc test (two sided) for epididymis and spinal cord, and by Kruskal–Wallis rank-sum test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test (two sided) for kidney. Viral loads were significantly higher for African than for Asian ZIKV strains in the brain (p < 0.0001), spinal cord (p < 0.0001), testis (p < 0.0001), kidney (p < 0.0001), and heart (p < 0.0001). e Infectious virus in brain and testis collected on day 7 post infection are shown in log10-transformed 50% tissue-culture infectious dose (TCID50) per mg of tissue. The horizontal dotted line indicates the lower limit of detection of the assay (310 TCID50 units per mg of tissue). Statistical significance of differences was determined by Kruskal–Wallis rank-sum test followed by Steel-Dwass’s post hoc test for brain and by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for testis. Infectious titers were significantly higher for African than for Asian ZIKV strains in the brain (p < 0.0001) and testis (p < 0.0001). In (d, e), data are presented as mean ± standard deviation and ZIKV strains not sharing a letter above the graph are statistically significantly different (p < 0.05). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.