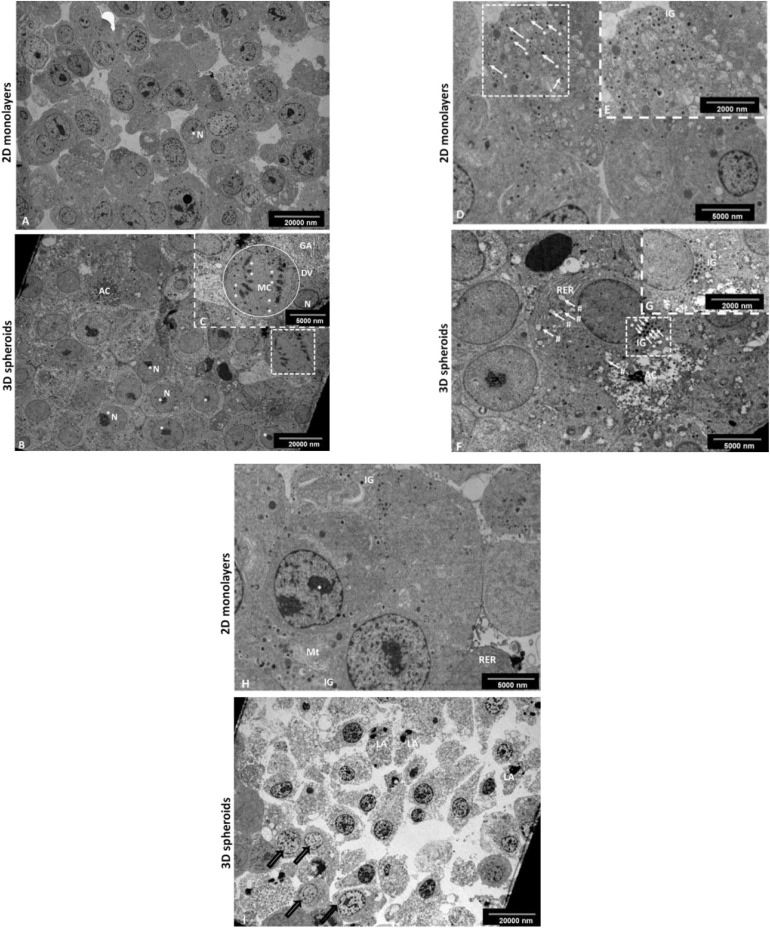
FIGURE 2.
Transmission electron micrograph of the INS-1 2D monolayer and 3D spheroids. Electron micrographs demonstrate some characteristic ultrastructural features synonymous with pancreatic β-cells. In 2D monolayers, cells presented with euchromatic nuclei containing multiple prominent nucleoli (A). In 3D spheroids, cells displayed euchromatic nuclei with prominent nucleoli (B); the occasional mitotic cell with chromosomes evident, RER and Golgi apparatus (insert, C). AC, Apoptotic cell; RER, Rough endoplasmic reticulum; N, Nucleus; *Nucleolus, **Chromosomes, Circle DV, dividing cell; GA, Golgi apparatus. Scale bars = 2,000 and 5,000 nm. Electron micrographs confirming the presence of characteristic insulin-like β granules. In 2D monolayers, electron micrographs demonstrate the presence of many insulin-like secretory β-granules (D and insert E). In 3D spheroids, cells displayed characteristic insulin-like β granules and the presence of an early apoptotic cell located next to the live cells with cytoplasmic RER and early signs of apoptosis including blebbing of mitochondria (F and insert G). White arrows (#), mitochondrial blebbing; AC, Apoptotic cell; RER, Rough endoplasmic reticulum; white arrows (*) IG, Insulin secretory β granules. Scale bars = 2,000 and 5,000 nm. In 2D monolayers, transmission electron micrograph showed the presence of ultrastructural features including of euchromatic nuclei, rough endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and IG (H). In 3D spheroids, EM showed an area of dead cells in various advanced stages of apoptosis marked with bold arrows (I). Scale bars = 5,000 and 20,000 nm.