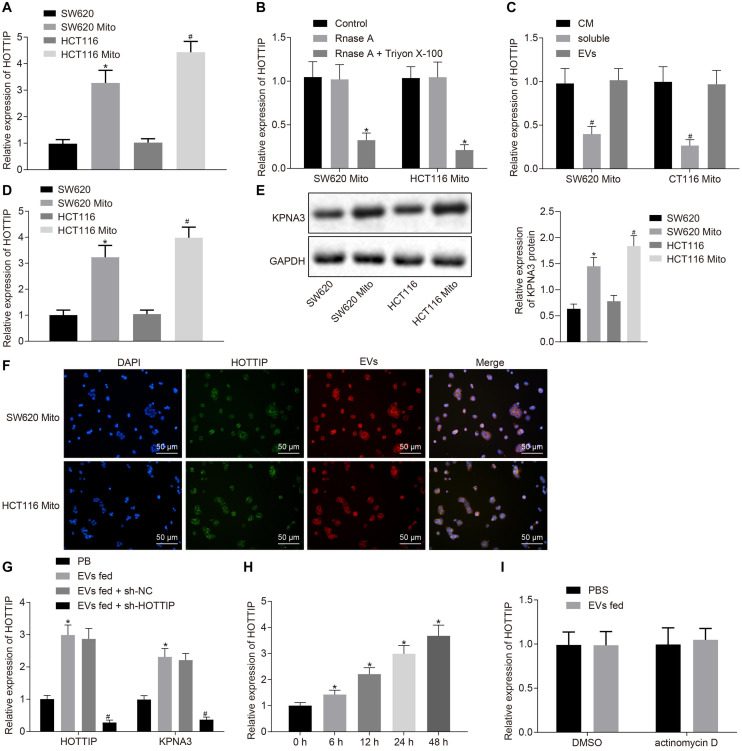
FIGURE 5.
HOTTIP is transferred from the EVs derived from mitomycin-resistant cells to parental cells. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of the level of HOTTIP in the CM of parental and mitomycin-resistant cells. (B) CM of SW620Mito cells and HCT116Mito cells were treated with RNase A (2 mg/ml) alone or in combination with Triton X-100 (0.1%) for 20 min. The levels of HOTTIP in the CM were determined by RT-qPCR. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of the levels of HOTTIP in the derived EVs, CM supernatant and whole CM of mitomycin-resistant cells. (D) RT-qPCR analysis of the level of HOTTIP in CM of mitomycin-resistant and parental cells. (E) KPNA3 expression in mitomycin-resistant cells and their derived EVs measured by Western blot analysis. (F) Confocal microscopic observation of fluorescence signal (scale bar = 50 μm). (G) Determination of HOTTIP and KPNA3 expression in the parental cells co-cultured with EVs derived from the mitomycin-resistant cells by RT-qPCR analysis. (H) RT-qPCR analysis of HOTTIP expression in the parental cells co-cultured with EVs derived from the mitomycin-resistant cells at different time points. (I) The parental cells treated with actinomycin D (1 μg/mL) were co-cultured with EVs for 48 h. HOTTIP expression in the parental cells determined by RT-qPCR. *p < 0.05 vs. the SW620 cells, control, cells treated with PBS or cells co-cultured with EVs for 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. the HCT116 cells, CM or parental cells co-cultured with EVs from the sh-NC-transfected mitomycin-resistant cells. Data (mean ± standard deviation) were analyzed by unpaired t test between two groups, and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple groups. The cell experiments were independently conducted in triplicates.