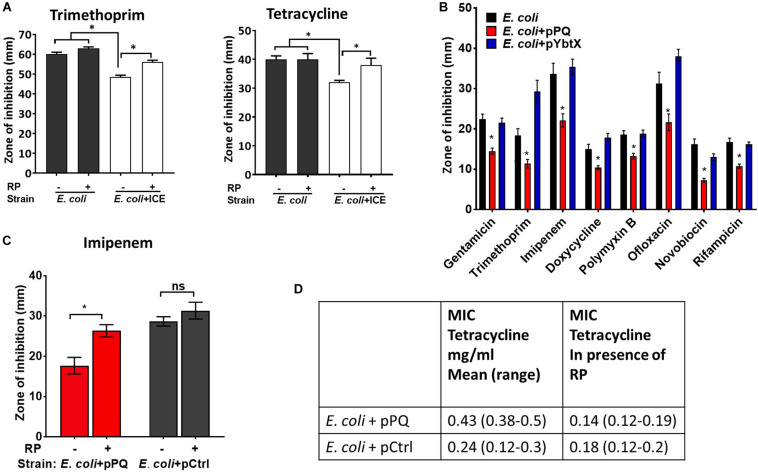
FIGURE 6.
Antimicrobial susceptibility of E. coli was reduced by ICEKp or by YbtPQ alone. (A) Transconjugant E. coli + ICE carrying the ICEKp was significantly less sensitive than E. coli to trimethoprim and tetracycline in a disk diffusion assay (25 and 10 μg per disk, respectively). Inhibition of efflux using reserpine (50 μg/disk) significantly increased the susceptibility of the transconjugant to each antimicrobial. Reserpine (RP) had no significant effect on the susceptibility of parental E. coli to either antimicrobial. (B) E. coli carrying plasmid pPQ, encoding YbtPQ, were significantly less susceptible to all antimicrobials tested, whereas control plasmid pYbtX had no significant effect on antimicrobial susceptibility. From left to right, disks contained 10 μg, 5 μg, 10 μg, 30 μg, 300 units, 5 μg, 30 μg, or 5 μg of antimicrobial. (C) The effect of YbtPQ on susceptibility to imipenem was reduced by reserpine. pCtrl indicates a control plasmid without ybtPQ (vehicle only control). Data are the mean and standard deviation of six replicates. Strains and conditions were compared by Student’s t test. * indicates p < 0.05. (D) The effect of YbtPQ on the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of E. coli for tetracycline was determined using E-test assay in the presence or absence of reserpine (RP 50 μg/ml) in triplicate (range tested was 0.016–256 μg/ml).