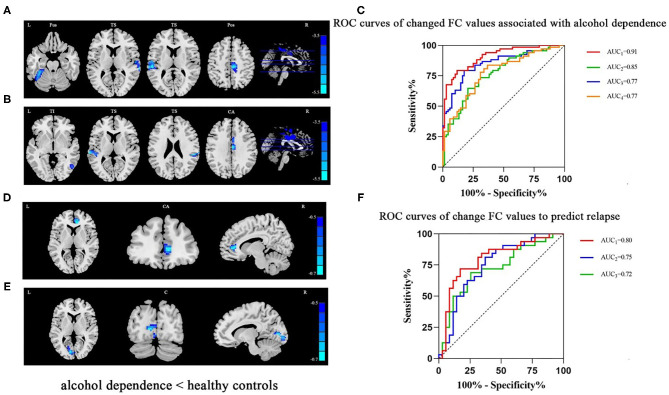
Figure 1.
(A) In patients with AD, lower FC was detected in the left fusiform, bilateral temporal superior and right postcentral areas (seed: NAc). (B) In patients with AD, lower FC was detected in the right temporal inferior, bilateral temporal superior and left cingulum anterior areas (seed: mPFC). (C) The ROC curves of logistic regression models using all three indicators (smoking status and two FC indicators, AUC1 = 0.91) or two FC indicators (AUC2 = 0.85), only FC between the NAc and left fusiform (AUC3 = 0.77), or only FC between the mPFC and left cingulum anterior (AUC3 = 0.77) to differentiate AD cases and HCs. (D) Among patients with AD who had relapsed based on the follow-up survey, lower FC in the right cingulum anterior (seed: NAc) was detected. (E) Among patients with AD who had relapsed, lower FC in the left calcarine (seed: mPFC) was detected. (F) The ROC curves of logistic regression models using both FCs (AUC1 = 0.80), only FC between NAc and right cingulum anterior (AUC2 = 0.75), or only FC between mPFC and left calcarine sulcus (AUC3 = 0.72) to predict relapse. Clusters were labeled with the Automated Anatomical Labeling (AAL) atlas. The t maps of (A,B) were drawn with a threshold of p < 0.001 at the voxel level and PFWE < 0.05 at the cluster level. Though the results of (D,E) could not exist relative to the above threshold, t maps of these results were shown with a threshold of p < 0.016 at the voxel level and PFWE < 0.05 at cluster level. The color bar indicates voxel-wise t values. lower FC is shown in blue. The brighter the blue, the lower the FC. FC, functional connectivity; NAc, nucleus accumbens; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; L, left; R, right; Fus, fusiform; TS, temporal superior gyrus; Pos, postcentral; TI, temporal inferior; CA, cingulum anterior; C, calcarine sulcus; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; AUC, area under curve; AD, alcohol dependence.