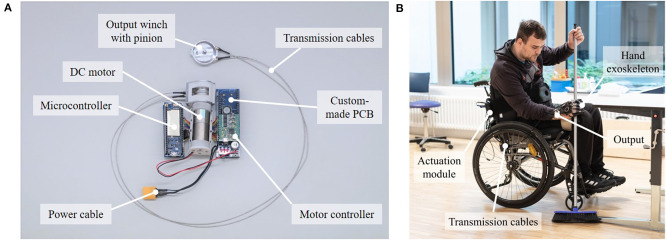
Figure 5.
Overview and use case of the developed cable-based RAS: (A) A DC motor actuates the pull–pull cable transmission system. At the output, rotational motion and torque are translated into linear motion and force via a rack-and-pinion mechanism. A microcontroller and motor controller, placed on custom-made printed circuit boards, control the motor current. (B) An SCI subject wears the hand exoskeleton actuated by the developed RAS to firmly grasp a broom. The fully wearable RAS integrated into the actuation module is mounted on the backrest of the wheelchair. The flexible transmission allows the user to move the arm freely.