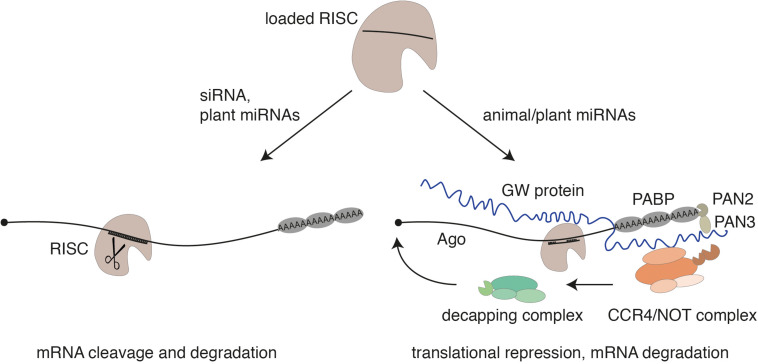
FIGURE 2.
The guide strand of the siRNA or a miRNA is loaded into an Argonaute protein. In case of a perfect complementarity through siRNAs or miRNAs (which is often observed in plants), a catalytically active Argonaute protein cleaves the mRNA as part of RISC (left). As miRNAs in animals are only partially complementary to their target RNAs, Slicer-facilitated cleavage is impaired. In this case, Argonaute recruits a member of the GW protein family. These proteins mediate the interaction with further downstream acting factors like poly-(A)-binding proteins (PABPs) or the deadenylase complexes PAN2/PAN3 and CCR4/NOT. This leads to translational repression, deadenylation, decapping, and 5′–3′ exonucleolytic decay of the mRNA. Translational repression by miRNAs has also been observed for plant miRNAs.