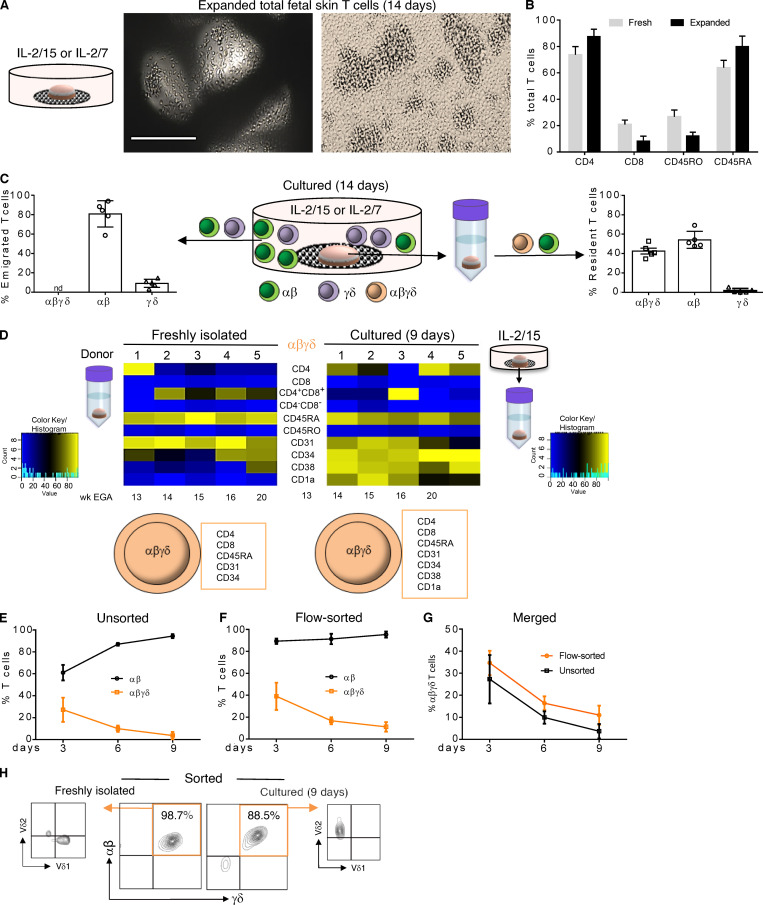
Figure 5.
Migration and expansion potential of fetal skin T cells ex vivo. (A) Upon culture of fetal skin biopsies on grids, huge T cell clusters were observed after 14 d. Scale bar, 200 µm. (B) Comparative analysis of freshly isolated and expanded fetal skin T cells using flow cytometry and indicated markers (n = 5). (C) Frequency of T cell subsets emigrated and expanded from fetal skin biopsies (left) and isolated from skin biopsies (right) after 14 d of culture. Mean ± SEM; nd, not detectable (n = 5). (D) Heatmap showing expression of indicated markers on DP αβγδ T cells isolated before culture and upon 9 d of organ culture (n = 5). (E–G) DP αβγδ in contrast to SP αβ fetal skin T cells did not expand in IL-2/15 conditioned medium. Unsorted, 13–21 wk EGA, n = 7; flow-sorted, 13–20 wk EGA, n = 5. (H) Vδ2 but not Vδ1 DP αβγδ fetal skin T cells can be expanded in the presence of IL-2 and zoledronate (n = 5).