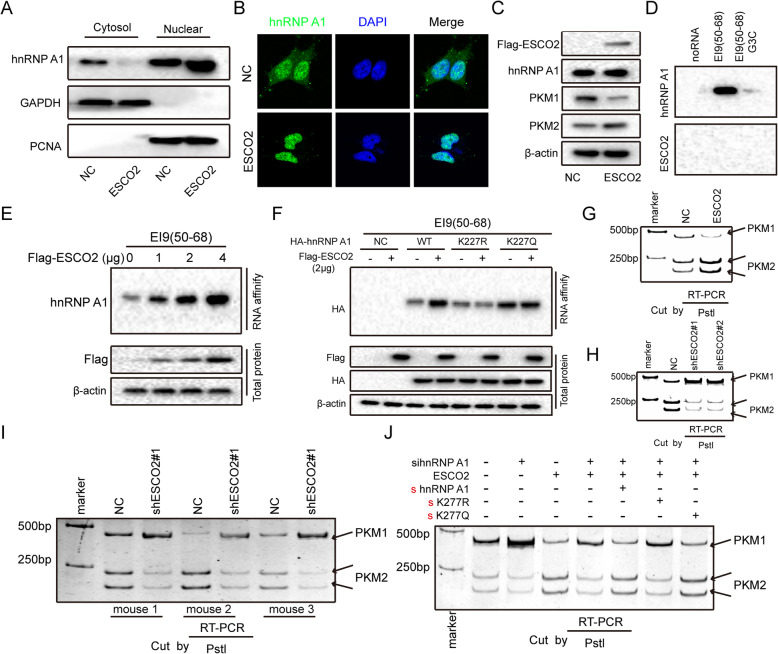
Fig. 6.
ESCO2 increases hnRNPA1 binding to the EI9 of PKM mRNA by inhibiting hnRNPA1 nuclear export, eventually inhibiting PKM1 isoform formation and inducing PKM2 isoform formation. a–c ESCO2-FLAGplasmid was transfected into NCI-H1975 cells; the nucleus and cytoplasm were separated, and then hnRNPA1 was detected using western blotting (a). Anti-hnRNPA1 antibody was used to detect the subcellular localization of hnRNPA1 (green) (b). Protein levels were detected using western blotting (c). d NCI-H1975 nuclear extracts were affinity-purified using biotin-labeled RNAs, and then ESCO2 and hnRNPA1 were detected. e ESCO2-FLAG vector was transfected into NCI-H1975 cells, RNA affinity purification was performed using biotin-labeled RNA EI9 (50–68), and then hnRNPA1 was detected. f WT hnRNPA1 and its mutant K277R and K277Q plasmids together with ESCO2 plasmids were co-transfected into NCI-H1975 cells, and RNA affinity purification was performed as in (d), and then hnRNPA1 was detected. g–j PKM splicing assay was performed by combining RT-PCR with PstI. g ESCO2-FLAG vector was transfected into NCI-H1975 cells, and then PKM splicing assay was performed. h The PKM splicing of NCI-H1975 cells with ESCO2 stable silencing was detected. i PKM splicing was performed in mouse xenograft tumors (n = 3). j After 36-h transfection of hnRNPA1 siRNAs into NCI-H1975 cells, the cells were transfected with WT hnRNPA1 and its mutant K277R and K277Q plasmids together with ESCO2 plasmids, and then the PKM splicing assay was performed