Figure 3.
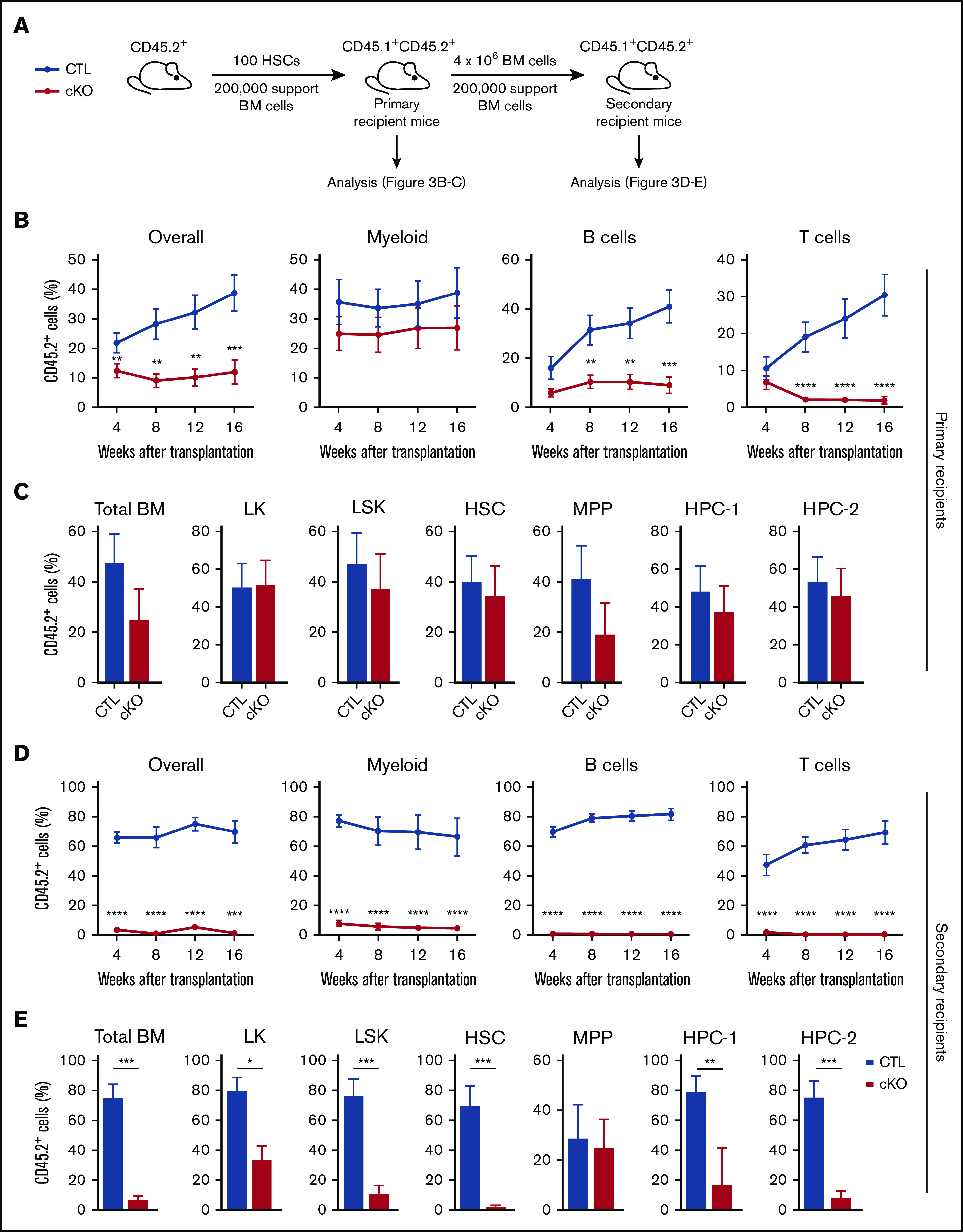
HSCs without JMJD6 fail to sustain multilineage hematopoiesis upon serial transplantation. (A) Experimental design. One hundred BM HSCs from 8- to 10-week-old Jmjd6cKO and Jmjd6CTL mice were transplanted into lethally irradiated syngeneic CD45.1+/CD45.2+ primary recipient mice together with 2 × 105 competitor CD45.1+ BM cells. After 16 weeks, 4 × 106 unfractionated BM cells from primary recipient mice were transplanted into lethally irradiated syngeneic CD45.1+/CD45.2+ secondary recipient mice together with 2 × 105 competitor CD45.1+ BM cells. PB of primary and secondary recipient mice was analyzed every 4 weeks and hematopoietic compartments were analyzed 16 weeks posttransplantation. (B) Percentage of CD45.2+ cells in the overall PB compartment, as well as the myeloid, B-cell, and T-cell compartments, in primary recipient mice (n = 2 per genotype; 4-5 recipients per group). (C) Percentage of CD45.2+ cells within the total BM, LK, LSK, HSC, MPP, HPC-1, and HPC-2 compartments of primary recipient mice 16 weeks after transplantation (n = 2 per genotype; 4-5 recipients per group). (D) Percentage of CD45.2+ cells in the overall PB compartment, as well as the myeloid, B-cell, and T-cell compartments, in secondary recipient mice (n = 2 per genotype; 4-5 recipients per group). (E) Percentage of CD45.2+ cells within the total BM, LK, LSK, HSC, MPP, HPC-1, and HPC-2 compartments of secondary recipient mice 16 weeks after transplantation (n = 2 per genotype; 4-5 recipients per group). Data represent mean ± SEM. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001, Mann-Whitney U test.
