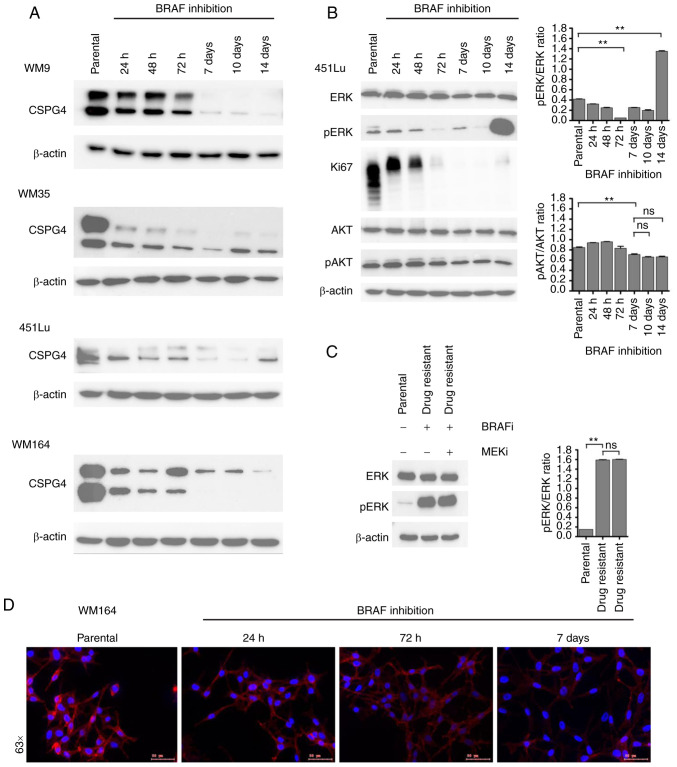
Figure 3.
Changes in CSPG4 expression over time upon BRAF inhibition. (A) WM9, WM35, 451Lu and WM164 cells were exposed to BRAF inhibitor (250 nM PLX4032) for 14 days. Samples were collected at indicated time points and CSPG4 (280 and 450 kDa) expression was analyzed in cell lysates by western blotting. β-actin (45 kDa) was used as a loading control. (B) Protein lysates of 451Lu parental and PLX4032-exposed cells were subjected to western blotting for expression levels of Ki67 (345/395 kDa), p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2; 42/44 kDa), phospho-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204; 42/44 kDa), total AKT (60 kDa), phospho-AKT (Ser473; 60 kDa). β-actin (45 kDa) was used as a loading control. Histograms represent pERK and pAKT expression normalized to ERK and AKT, respectively (right panels). Statistical analysis was carried out using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. **P<0.001; ns, not significant. (C) Lysates of 451Lu parental and PLX-resistant cells, exposed to BRAF and/or MEK inhibitor (250 nM PLX4032 and/or 5 nM GSK1120212, respectively) were subjected to western blotting to detect p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2; 42/44 kDa) and phospho-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204; 42/44 kDa). β-actin (45 kDa) was used as a loading control. Histogram represents pERK expression normalized to ERK (right panel). Statistical analysis was carried out using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. **P<0.001; ns, not significant. (D) Immunofluorescent labelling of CSPG4 in WM164 parental and 1,000 nM PLX4032-exposed cells was performed using anti-CSPG4 9.2.27 mAb and goat anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 568®. CSPG4, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4.