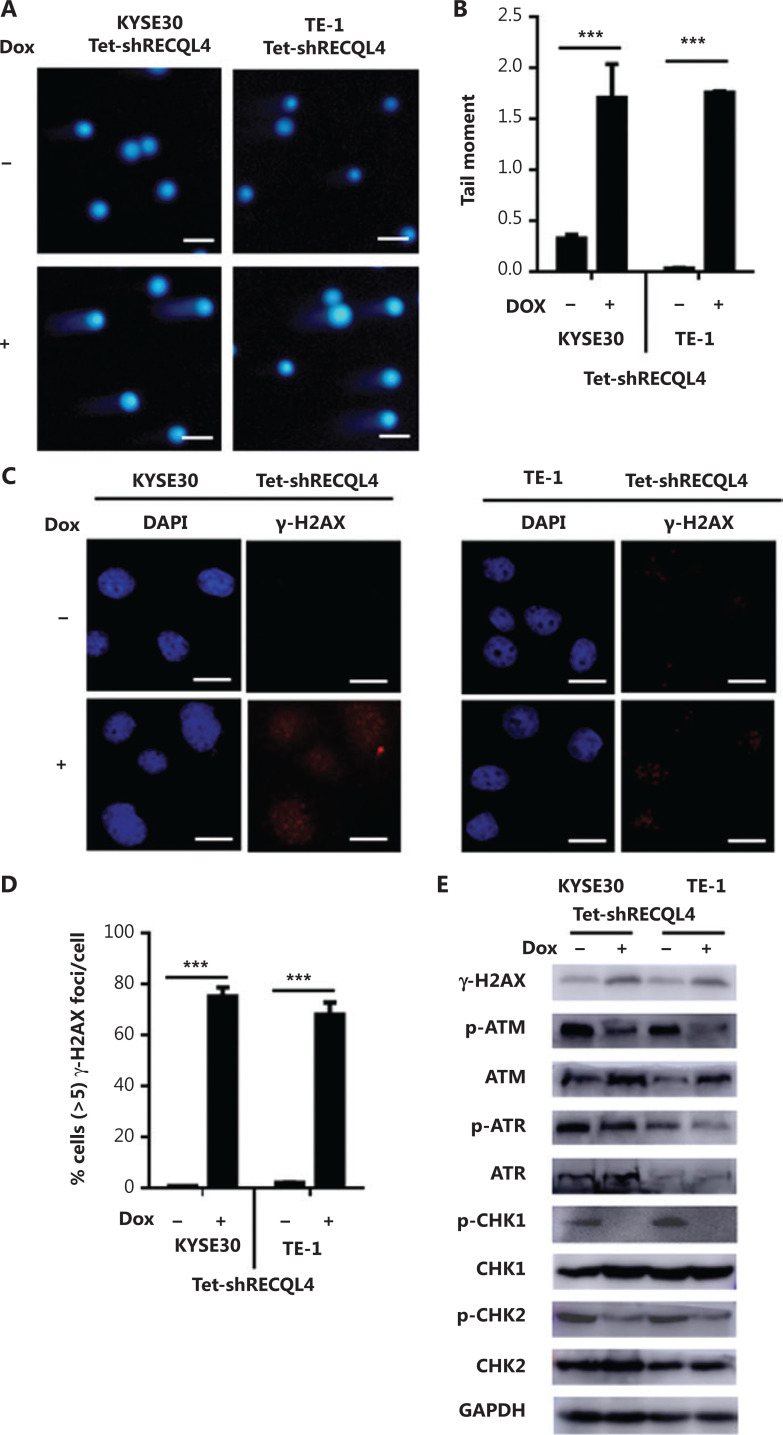
Figure 7.
Depletion of RECQL4 causes DNA damage, but impairs the DNA damage response in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells. (A) Stable Tet-on inducible RECQL4 knockdown cell lines (KYSE30 and TE-1 cells) (+Dox) and controls (–Dox) were analyzed using the alkaline comet assay, and the tail moment was calculated as the percentage DNA in the tail multiplied by the tail length, with a microscopic magnification at ×200. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Statistical analysis of the data derived from (A). ***P < 0.001. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of γ-H2AX in stable Tet-on inducible RECQL4 knockdown cell lines (KYSE30 and TE-1 cells) (+Dox) and controls (–Dox). Microscopic magnification (×400), Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) Distribution of cells with at least 5 γ-H2AX foci. For each group 500 cells were counted. Shown are the averages and SD of 3 repeats. ***P < 0.001. (E) Western blot analysis of γ-H2AX, p-ATM, ATM, p-ATR, ATR, p-CHK1, CHK1, p-CHK2, and CHK2 protein levels in stable Tet-on inducible RECQL4 knockdown cell lines (KYSE30 and TE-1 cells) (+Dox) and controls (–Dox).