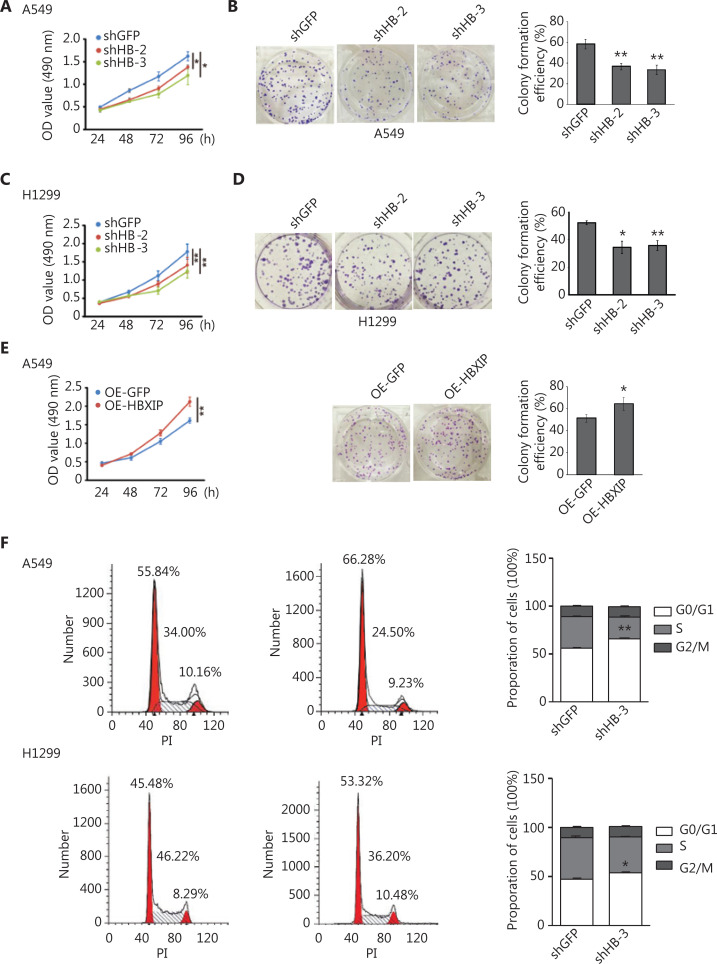
Figure 2.
HBXIP promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression in vitro. (A) and (C) Cancer cell viability was examined using the MTS assay in HBXIP stable knockdown cells and control cells. (B) and (D) The colony formation assay was performed in HBXIP stably knocked down cells. A549 and H1299 cells were cultured for 12 days prior to Crystal Violet staining. (E) Left panel; the viability of HBXIP-overexpressing A549 cells was examined using the MTS assay. Right panel; representative images of forming colonies and their estimated numbers. HBXIP-overexpressing and control A549 cells were fixed and stained 12 days after seeding. (F) Cell cycle analysis of HBXIP-deficient cells. The numbers of viable A549 and H1299 cells in the G0/G1, S, and G2/M phases were individually quantified by flow cytometry. Representative profiles (left panel) and the corresponding percentages of each stage are shown. The results were analyzed by an unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.