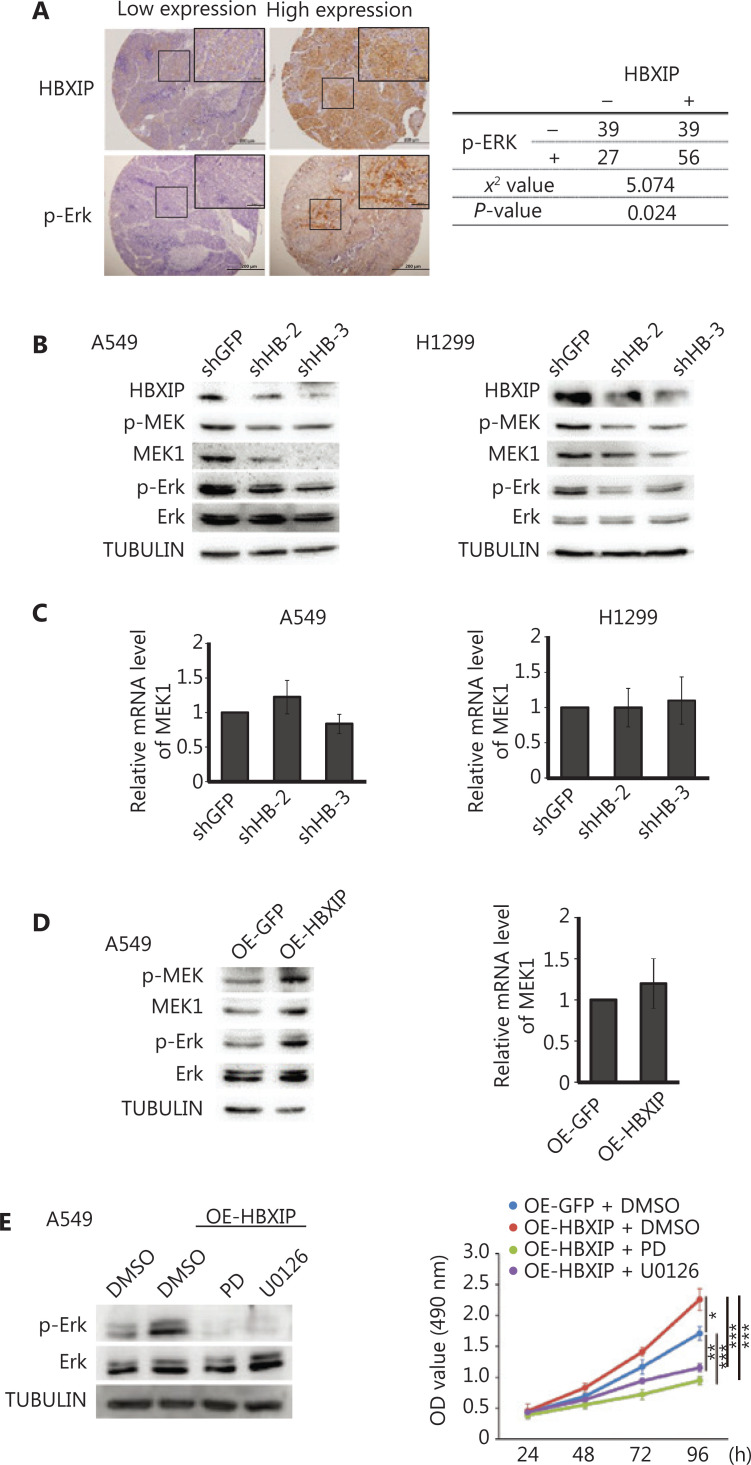
Figure 3.
HBXIP promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through the MAPK/ERK pathway. (A) Phosphorylated ERK levels in the NSCLC cohort samples were analyzed by immunohistochemical staining, and the correlation between p-ERK and HBXIP was analyzed. (B) Phosphorylated MEK and ERK levels in HBXIP-deficient A549 and H1299 cells were analyzed by Western blot. (C) MEK1 mRNA levels in HBXIP knockdown A549 and H1299 cells were examined by RT-qPCR. (D) Western blots of phosphorylated MEK and ERK levels (left panel) and MEK1 mRNA levels in HBXIP-overexpressing A549 cells. (E) Phospho-ERK levels in HBXIP-overexpressing A549 cells treated with PD (10 μM) or U0126 (10 μM) for 24 h were determined by Western blot analysis. (E) MTS assay measuring the viability of HBXIP-overexpressing A549 cells treated with PD (10 μM) or U0126 (10 μM) for the indicated times. The results were analyzed by an unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001.