Figure 4. Long-read data improves genome assembly.
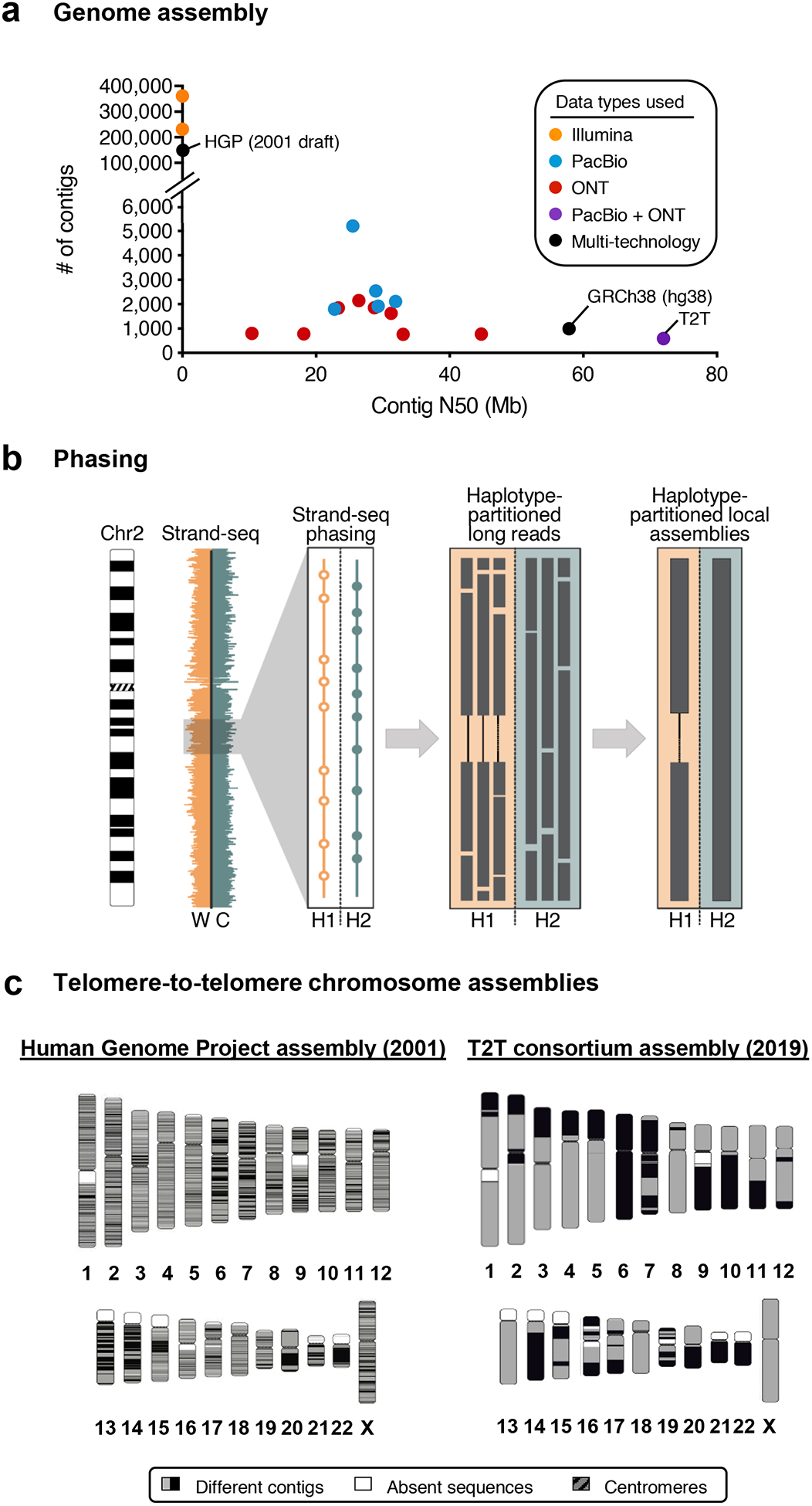
a) The plot shows the number of contigs and the contig N50 for 18 unphased human genome assemblies listed in Table 2. Genomes assembled from long-read data (PacBio or ONT) have fewer contigs and higher contig N50s compared to those assembled from short-read data (Illumina). Combining long-read data types (PacBio + ONT) produces a genome assembly with even fewer contigs and a higher contig N50, surpassing that of the reference genome (GRCh38, hg38) in contiguity. b) The schematic illustrates a genome assembly phasing approach known as Strand-seq164. In this approach, the template strand [i.e. the Watson (W, orange) or Crick (C, teal) strand)] is sequenced via short-read sequencing to generate template-specific short reads. When the W and C template strands are inherited from either parent, these templates-specific reads can be assigned to either parental homologue based on the direction they map to a genome assembly. For example, here, we show Strand-seq reads aligned to chromosome 2 and binned in 200 kb genomic stretches (orange and teal bars). Strand-seq reads containing a haplotype-specific SNP are able to partition long reads into haplotype 1 (H1, empty circles) or haplotype 2 (H2, filled circles). Haplotype-partitioned long reads permit the detection of structural variation, such as the deletion in H1 shown here, and can be assembled to generate haplotigs that span the region, thereby generating a phased genome assembly. c) Chromosome ideograms are shown that compare the 2001 Human Genome Project assembly (hg1)72 and the 2019 T2T assembly (CHM13 rel3 assembly). hg1 had >145,000 gaps and nearly 150,000 contigs, whereas the rel3 assembly has <1000 gaps and <1000 contigs (see Table 2 for additional statistics). Contigs are represented by alternating black and gray blocks, absent sequences are represented by white blocks, and centromeres are represented by red blocks.
