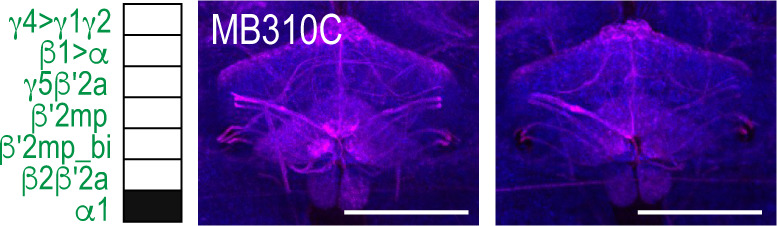
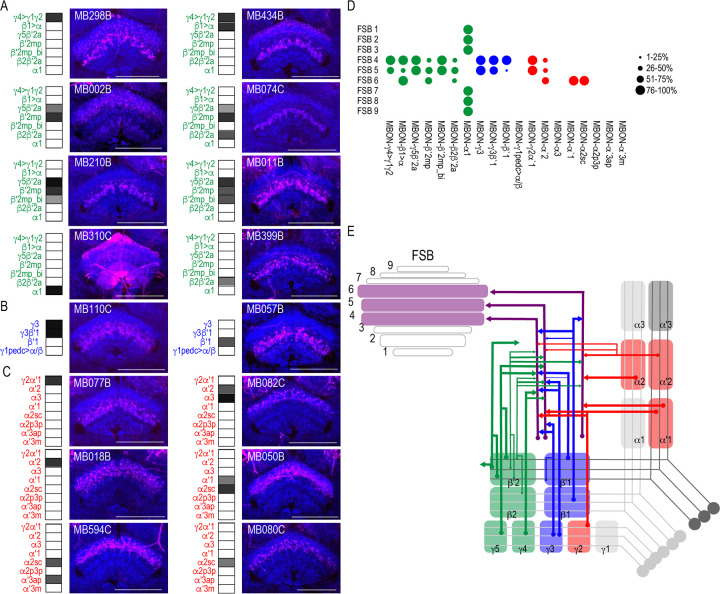
Figure 5. MBONs converge on different layers of the FSB.
Exemplar max-stacks of glutamatergic (A), GABAergic (B), and cholinergic (C) MBONs whose postsynaptic neurons innervate the FSB. Max-stacks are approximately 50 μm thick. Slices were selected based on the relative position of the FSB. For FSB stacks: magenta, postsynaptic trans-Tango signal, blue, brp-SNAP neuropil. Map of MBONs accompany each exemplar with the relative expression pattern (grayscale, 1–5) accordingly to FlyLight. For each map, green=glutamatergic, blue=GABAergic, red=cholinergic. Scale bar = 50 μm. (D) Map summarizing the percentage of trans-Tango-positive signal in each FSB layer across brains for each MBON. (E) Schematic depicting MBONs that converge onto different layers of the FSB. MB compartments are colorized based on the neurotransmitter expressed by the MBON that innervates it. Lines thickness corresponds to the percentage of trans-Tango-positive signal in each FSB layer across brains for each MBON.
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. MBON α1 postsynaptic signal innervating FSB in females.