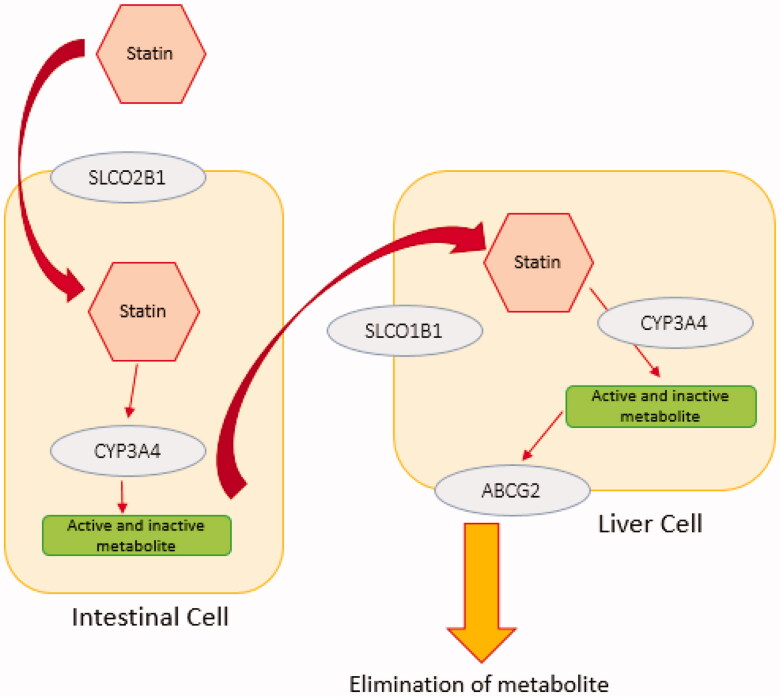
Figure 1.
The simple schematic pathway for statin transporters. Statins undergo passive intestinal absorption and subsequently are taken up from the blood stream into the liver by members of solute carrier transporter family (SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3, SLCO2B1). Statins are metabolised by phase I and II enzymes and eliminated via efflux transporters mediated biliary excretion. Different enzymes are involved in phase I statin metabolism such as CYP3A4. Elimination of statins is carried out by members of the efflux family transporters ABCB1, ABCC2, ABCG2 or ABCB11. Statin metabolism and elimination take place primarily in the liver and to a lesser extent in the kidney.