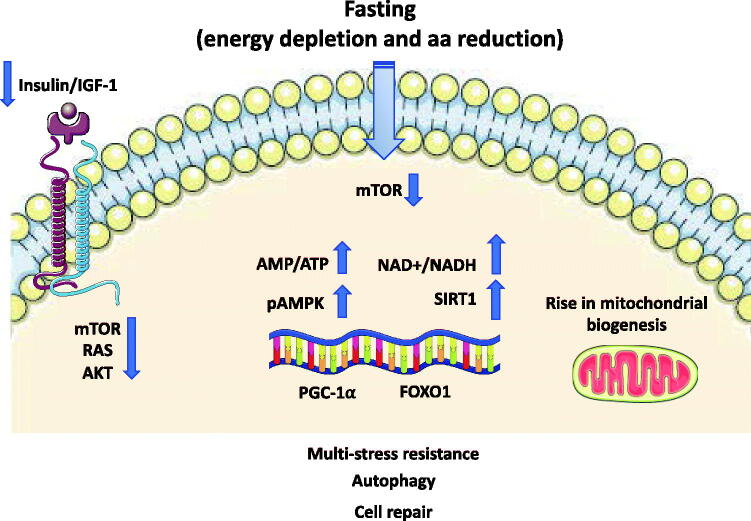
Figure 2.
Representationof signalling pathways modulated fasting. The reduced levels of circulating amino acids and of IGF-1 consequent to fasting repress the activity of mTOR and its downstream effector leading to an inhibition of global protein synthesis and promote recycling of macromolecules by autophagy stimulation. There is a rise in the AMP-to-ATP ratio leading to the activation of AMPK. SIRT1-driven deacetylation of PGC-1α and FOXO1 transcription factors provides a mechanism by which mitochondrial and lipid oxidation genes can be dynamically controlled in response to energy demand. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; FOXO1: forkhead box O1; IGF: insulin-like growth factor; NAD+: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; PGC-1α: peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ coactivator 1α; mTOR: mammalian target of Rapamycin; SIRT: sirtuin.