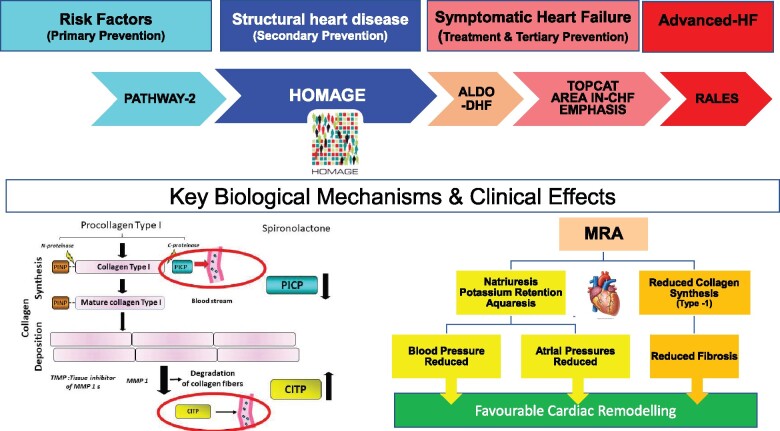
Take home figure:
Diagram showing the evolution from risk factors, through structural heart disease to heart failure and the randomized controlled trials of mineralo-corticoid receptor antagonists (MRA) that have addressed each stage. The PATHWAY-2 trial39 demonstrated the effects of spironolactone on blood pressure, a key risk factor for heart failure. HOMAGE is the only trial, to date, that has focused on patients with structural heart disease with few or no symptoms of heart failure. The ALDO-DHF trial14 showed favourable effects on ventricular filling in patients with a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and heart failure (HFpEF). Many patients in ALDO-DHF had less severe cardiac dysfunction than in HOMAGE; there is substantial overlap in the patient characteristics of these two trials. TOPCAT15 investigated the effects of spironolactone in HFpEF with equivocal results. EMPHASIS,13 AREA IN-CHF,34 and RALES9 investigated the effects of mineralo-corticoid receptor antagonists in HFrEF (heart failure with a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction). In HOMAGE, spironolactone caused an early reduction in weight, blood pressure, and natriuretic peptides, suggesting a natriuretic and diuretic effect. Changes in serum markers of type-1, although not type-III, collagen metabolism were also observed within 1 month. This combination of effects was followed by favourable cardiac remodelling. Type-1 collagen is the more important contributor to myocardial stiffness. The magnitude of changes in collagen metabolites observed suggests a systemic effect of spironolactone rather than only on the myocardium.