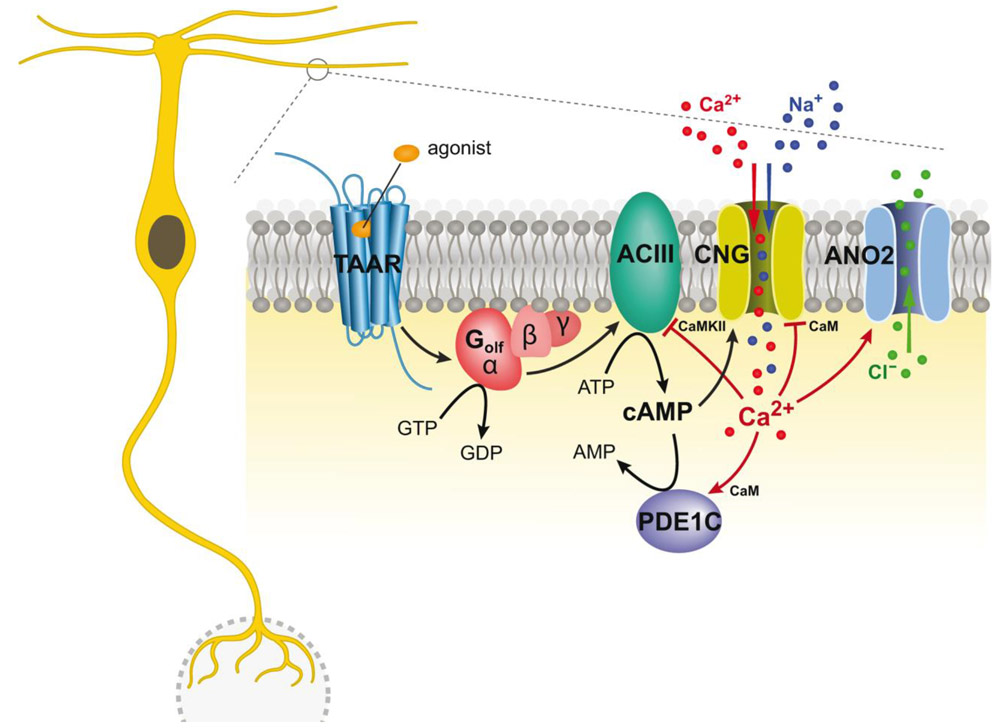
Figure 2.
The TAAR signal transduction cascade. Activation of a TAAR triggers an increase in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) through the activation of the receptor coupled G-protein (Golf) and adenyl cyclase type III (ACIII). Activated by the cAMP, cyclic nucleotide-gated channels (CNG) cause a depolarizing influx of both calcium (Ca2+) and sodium (N+) ions. This transient increase in Ca2+ opens a calcium-activated chloride channel anoctamin 2 (ANO2) causing an efflux of chloride (Cl−) ions that further amplifies the response. Phosphodiesterase 1C (PDE1C) hydrolyzes the cAMP, terminating its action.