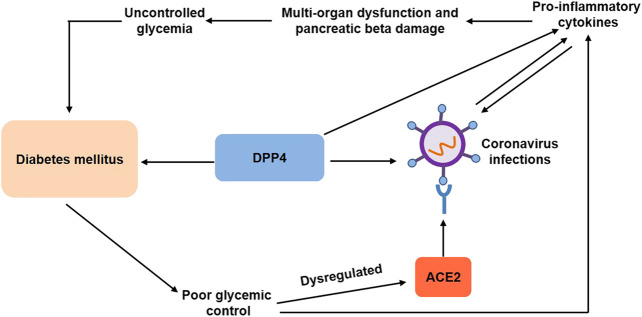
FIGURE 1.
Associations between diabetes mellitus and coronavirus infections. Diabetes mellitus contributes to poor glycemic control, which has been shown to dysregulate ACE2 glycosylation and increase proinflammatory cytokines, facilitating viral cell entry. Preexisting proinflammatory state, in turn, predisposes patients to coronavirus infections and aggravates multiorgan dysregulation and pancreatic beta damage, leading to uncontrolled glycemia and diabetes mellitus. DPP4, a common pharmacological target for type 2 diabetes, is also a functional coronavirus receptor, which increases the susceptibility to coronavirus infections. On the other hand, DPP4 exerts proinflammatory activity. DPP4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; ACE2, angiotensin converting enzyme 2.