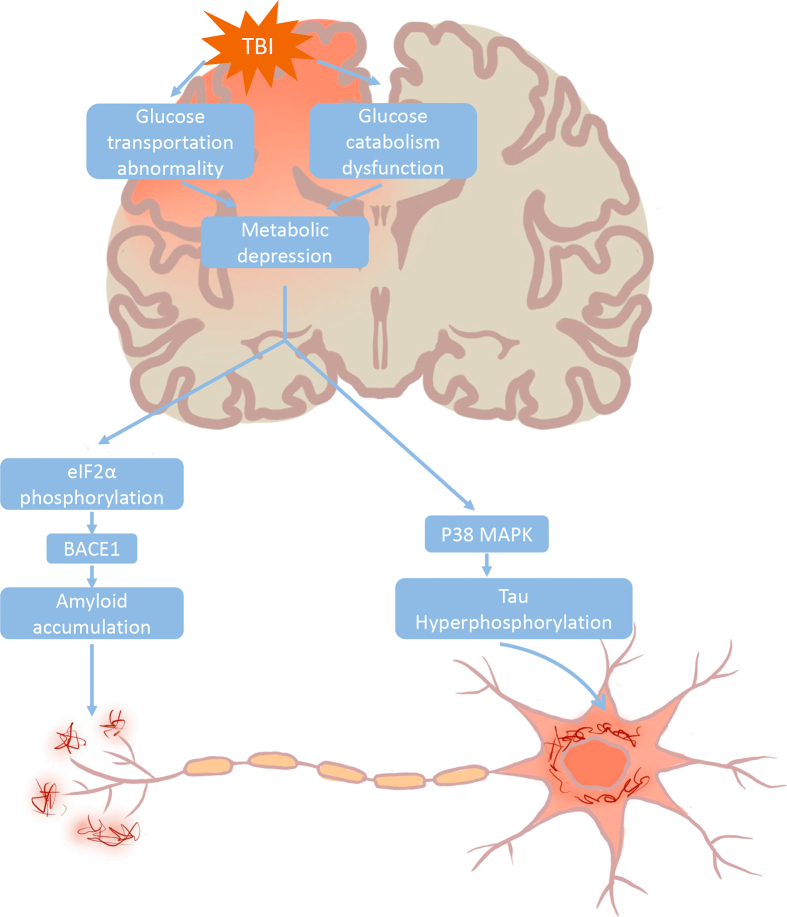
Fig. 2.
Hypothetical pathogenic cascades linking TBI and Alzheimer’s disease. TBI perturbs cerebral glucose metabolism by affecting glucose transportation and intracellular glucose catabolism, thereby resulting in metabolic depression. Reduced energy availability triggers eIF2α phosphorylation and in turn enhances the translation of BACE1, which ultimately leads to amyloidogenesis. On other hand, energy deprivation could induce activation of p38 MAPK cascade and consequent hyperphosphorylated tau protein, which eventually no longer binds microtubules and aggregates into intracellular neurofibrillary tangles.
TBI: traumatic brain injury; BACE: β-site APP cleaving enzyme; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase.