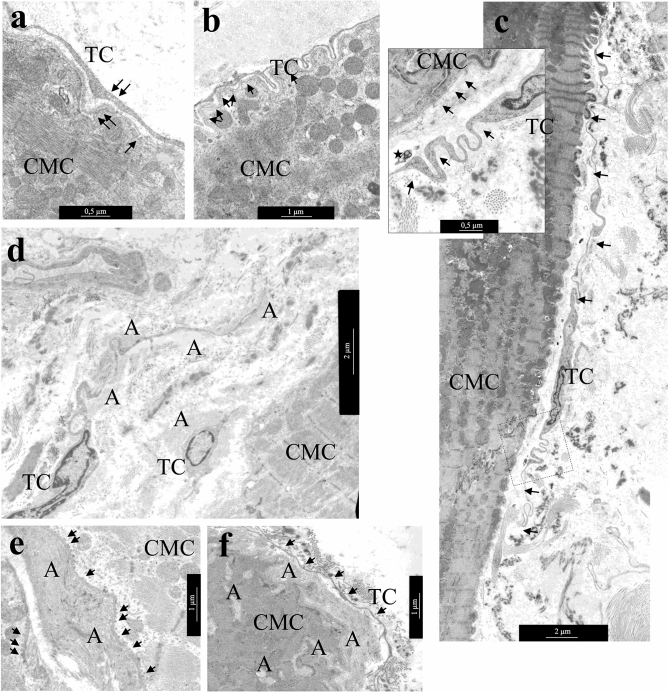
Figure 5.
Distance interactions of TCs and cardiomyocytes. (a) The caveolae in the membrane of cardiomyocyte and TC process (arrows). bar 500 nm. (b) The process of TC follows all surface curves and is distributed in the invagination of the T-system of cardiomyocytes. Note the caveolae on the sarcolemma of a cardiomyocyte (arrows). bar 1 µm. (c) TC with extended Tps (arrows) located along the cardiomyocyte surface. bar 2 µm. Insert—Several caveolae on the surface of cardiomyocyte and TC (arrows). A multivesicular body (asterisk) in the interstitium next to the process of the TC. bar 500 nm. (d–f) TCs in areas of amyloidosis. (d) TCs and their processes are surrounded by amyloid fibrils. bar 2 µm. (e) Accumulation of amyloid fibrils on the surface of the cardiomyocyte membrane. Multiple vesicles (arrows) on the inner surface of the sarcolemma of the cardiomyocyte. (f) Amyloid fibrillar deposits on the surface of the cardiomyocyte membrane and in invaginations of the T-system of the cardiomyocyte. The TC process (arrows) at a distance from the cardiomyocyte membrane. (e,f)—bar 1 µm. TEM. TC—telocyte, CMC—cardiomyocyte, A—amyloid fibrils.