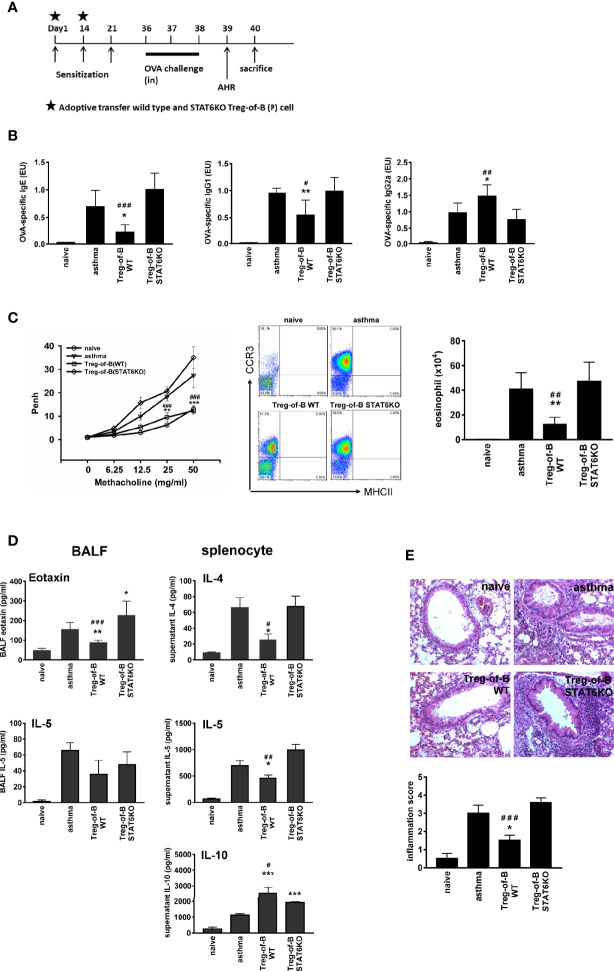
Figure 4.
STAT6 deficient Treg-of-B (P) cells did not exert therapeutic effect on allergic asthma. (A) Sensitization protocol. Mice were primed on days 1, 14 and 21 and challenges were performed on days 36–38. The Wild type Treg-of-B (P) cells or STAT6 knockout Treg-of-B (P) cells were adoptively transferred into mice on day 1 and 14 (2.5 × 106/mouse). Forty-eight h later, mice were sacrificed and parameters were analyzed. Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) was assessed one day prior sacrifice. (B) Serum was collected to measure the levels of OVA-specific IgE, IgG1 and IgG2a. The antibody concentrations in the standard serum were arbitrarily set to 1 ELISA unit (EU), where EU = (a sample – a blank)/(a positive – a blank). (C) The airway hyperresponsiveness following methacholine (MCh) challenge was performed and infiltrated eosinophils (MHCII- CCR3+) in bronchial alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was evaluated. (D) The IL-4, 5, and 10 and eotaxin levels in BALF and in the splenocyte culture supernatants were determined by ELISA. (E) Histological examination. Pulmonary tissue section of different groups stained with H&E and inflammation score was determined as described in Materials and Methods. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Data are representative of three different experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, compared with the asthma group. #p < 0.05 ##p < 0.001, ###p < 0.005, compared Treg-of-B STAT6KO group.