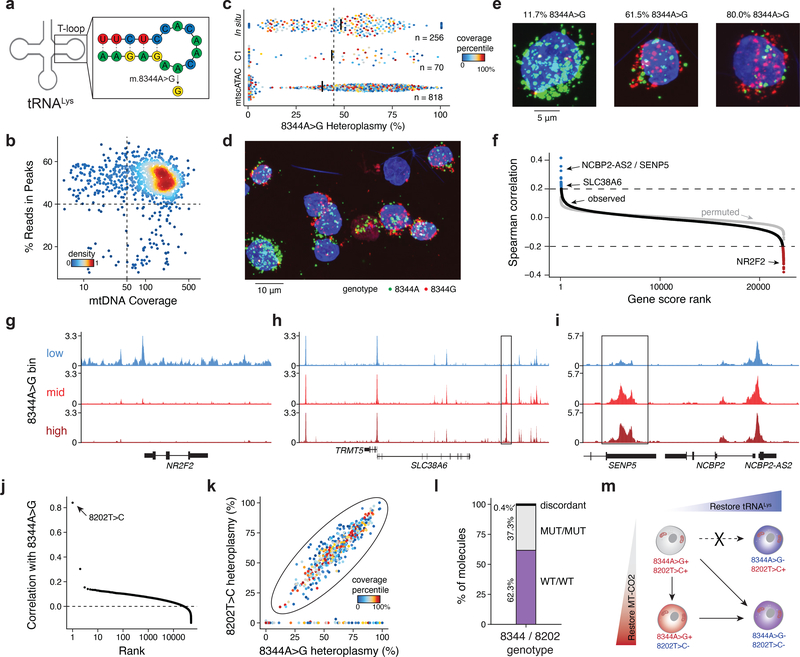
Figure 2 -. Pathogenic mtDNA variability and clonal evolution in cells derived from a patient with MERRF.
(a) Schematic of the mitochondrial lysine tRNA secondary structure with sequence and the pathogenic single nucleotide variant (8344A>G). (b) Quality control filtering for GM11906 single cells based on mean mtDNA genome coverage and percentage of nuclear reads in chromatin accessibility peaks. (c) Quantification of 8344A>G heteroplasmy variability in single GM11906 cells across three technologies. Numbers (n) of cells plotted are shown. Color represents the within-assay coverage percentile. Black bars indicate the median heteroplasmy per technology; the dotted line presents the mean heteroplasmy as determined for bulk ATAC-seq. (d) Field of view for in situ genotyped GM11906 cells, highlighting (e) single cells with low, medium, and high heteroplasmy as indicated for the pathogenic allele. Representative image selected from one of seven fields of view for one experiment. (f) Per-gene score Spearman correlations with the 8344A>G allele heteroplasmy. The grey dots show values for a permutation. Pseudo bulk chromatin accessibility track plots are shown for the (g) NR2F2, (h) TRMT5, and (i) SENP5/ NCBP2-AS2 loci. Pseudo-bulk groups were binned based on 0–10% (low), 10–60% (mid), and 60–100% (high) 8344A>G heteroplasmy. (j) Per-mutation heteroplasmy correlation with 8344A>G allele. The 8202T>C mutation is highlighted as the most correlated mutation. (k) Single-cell heteroplasmy for two indicated mutations. The circled population represents a double-positive population for both mutations. (l) Abundances of each variant on single molecule sequencing reads in the double positive population. (m) Schematic of the co-evolution of two subclonal populations marked by indicated mutations detected based on single-cell genotyping data. Putative cell transitions are indicated with solid arrows that may be a result of selective pressure of the pathogenic variant or genetic drift.