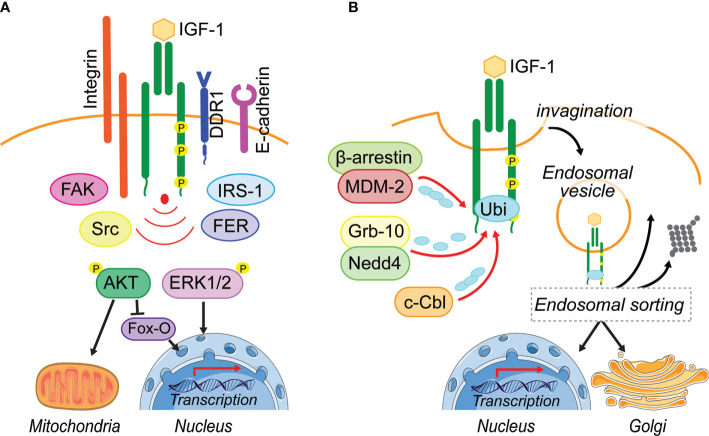
Figure 1.
Leaving the plasma membrane. (A) Located on the plasma membrane, activated IGF-1R induces two major pathways, PI3-K/AKT and MAPK/ERK1/2, to regulate cellular processes including metabolism and transcription. Different adhesion related kinases (FAK, Src, FER) and interacting proteins (IRS-1, DDR1) regulate IGF-1R endocytosis and thereby prolong or reduce IGF-1R signaling from the cell surface. In addition, these IGF-1R interacting proteins can enhance bias IGF-1R signaling or their cooperation is needed for the activation of IGF-1-induced pathways (Integrin). (B) Ligand-induced IGF-1R activation leads to the recruitment of E3-liages (MDM-2, Nedd4, c-Cbl) that can initiate IGF-1R poly- and mono-ubiquitination. Via membrane invagination and formation of clathrin- and caveolin-coated pits, the IGF-1R enters the cell in endosomal vesicles. It is assumed that the endosomal sorting system decides, whether IGF-1R gets degraded, travels back to the plasma membrane or translocates to intracellular membrane compartments. To this day it is unknown how the post-endocytotic IGF-1R translocation to intracellular membrane compartments, such as the Golgi and the nucleus is regulated and whether IGF-1R regulation of mitochondrial function is exclusively due to signaling transduction. Figure elements adapted from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com/), under license CC-BY3.0.