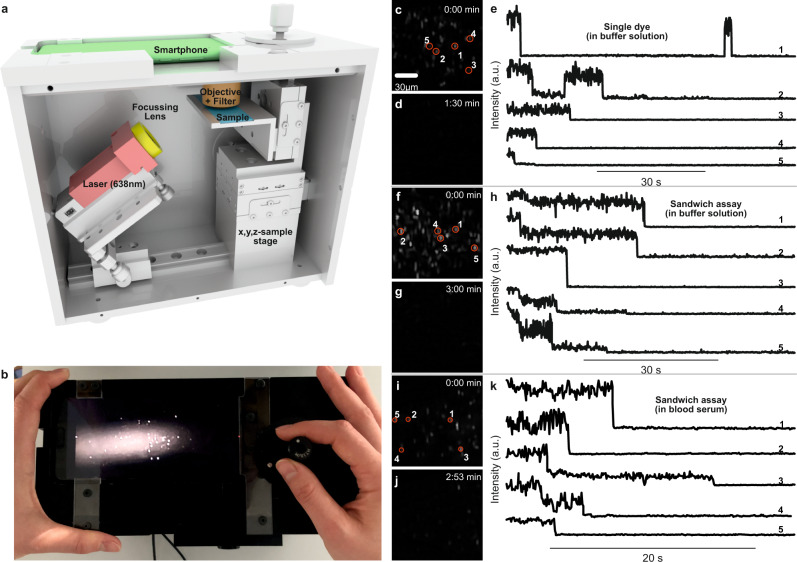
Fig. 3. Single-molecule detection on a portable smartphone microscope.
a Sketch of the portable smartphone microscope with the battery driven 638 nm laser (red), the focusing lens (f = 5 cm) (yellow), the microscope coverslip with the sample (blue), the objective lens and the emission filter (brown), and the smartphone monochrome camera as detector (green). b Top view photograph of the portable smartphone microscope. c Background corrected fluorescence image of NACHOS with 100 nm silver nanoparticles and a single Alexa Fluor 647 dye. d Fluorescence image as in c after illumination for 1:30 min. e Exemplary fluorescence transients of a single Alexa Fluor 647 in NACHOS measured on the portable microscope setup. Single bleaching steps of dyes and long-time blinking events are visible. f Background corrected fluorescence image of NACHOS equipped with a sandwich assay with 100 nm silver nanoparticles and Alexa Fluor 647 imager strands. g Fluorescence image as in f after illumination of the area for 3:00 min. h Exemplary fluorescence transients of Alexa Fluor 647 in a three-capture-strand DNA origami nanoantenna measured on the portable smartphone microscope. i Background corrected fluorescence image of NACHOS equipped with the sandwich assay with 100 nm silver nanoparticles and Alexa Fluor 647 imager strands after incubation in blood serum. j Fluorescence image as in i after illumination of the area for 2:53 min. k Exemplary fluorescence transients of Alexa Fluor 647 in a three-capture-strand NACHOS measured on the portable smartphone microscope. Fluorescence transients with one, two, and three bleaching steps (analogous to single-molecule confocal measurements) were observed. The movies represented in the panels c, d, f, g, i and j were reproduced at least 5 times. Three movies for each measurement are provided in the Supplementary Movies. The fluorescence transients shown in panels e, h and k were extracted from a single movie.