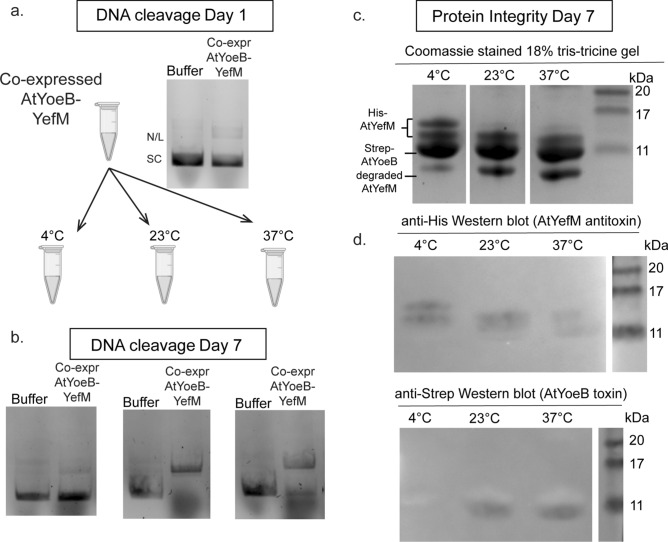
Figure 3.
The AtYefM antitoxin blocks AtYoeB-mediated DNA cleavage, but it readily undergoes degradation that releases AtYoeB catalytic activity. (a) DNA degradation is not present for 10 µM co-purified AtYoeB-YefM complex immediately after purification. (b) After incubation for 1 week at temperatures above 4 °C, however, DNA cleavage activity is apparent. (c) Electrophoretic analysis of the protein samples used in panel (b) reveals degradation of one of the protein components that increases after storage at 23 °C and 37 °C (relative to 4 °C). Resolution of the doublet for intact AtYefM antitoxin requires a high percentage (18%) tris-tricine acrylamide gel. (d) Western blots were used to identify the individual bands visualized in the gel in panel (c), revealing that the degraded component is the His-tagged AtYefM antitoxin, while the Strep-tagged AtYoeB toxin remains unchanged. Note that the lowest band that accumulates is likely degraded AtYefM antitoxin, which appears to no longer carry the N-terminal His tag. (Full images of blots are provided in Fig. S6).