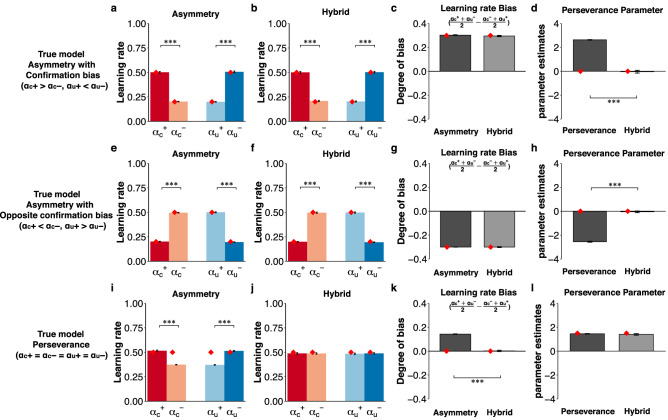
Figure 3.
The results of the simulation in the counterfactual learning context. (a–d) The results of the true model with asymmetric learning rates assuming confirmation bias (). (e–h) The results of the true model with asymmetric learning rates assuming opposite confirmation bias (). (i–l) The panel shows the results of the true model with symmetric learning rates () and choice perseverance (φ = 1.5). (a,e,i) The first column indicates the learning rates (, , ) in the Asymmetry model. (b,f,j) The second column indicates the learning rates in the Hybrid (gradual) model. (c,g,k) The third column indicates the degree of confirmation bias . (d,h,l) The final column shows the perseverance parameter (φ) in the Perseverance (gradual) and Hybrid (gradual) models. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05. The error bars represent the standard error of the mean. The diamonds denote the ground-truth value of the parameters used in the data generation.