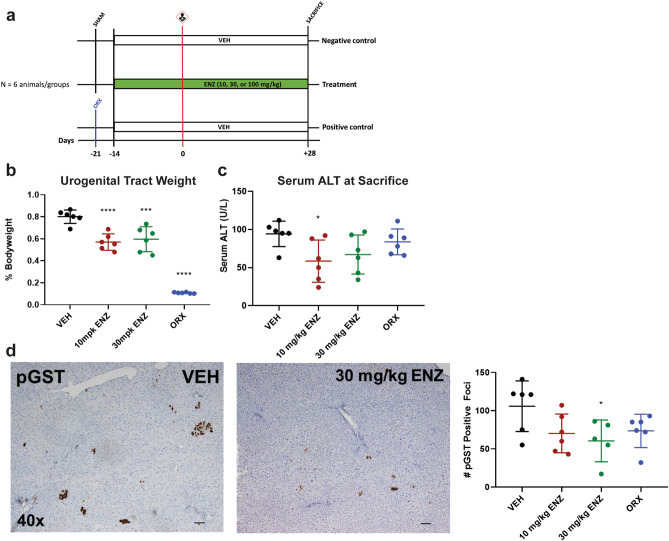
Figure 1.
Low dose, preventive ENZ inhibits DEN-induced hepatocellular carcinogenesis. (a) Study Design—simplified timeline highlighting preventive anti-androgen interventions. Carcinogen challenge consisting of the described DEN/PH/DEN procedure is represented by carcinogen pictogram. SHAM, sham castration; ORX, castration. Enzalutamide (ENZ) groups received 10, 30, or 100 mg/kg and control groups received vehicle (VEH), all once daily by oral gavage. Carcinogen-challenged, preventive ORX served as anti-androgen phenotype positive controls; carcinogen-challenged, SHAM rats served as anti-androgen phenotype negative controls. (b) Low-dose ENZ maintained an anti-androgen effect on bodyweight-normalized urogenital tract weights. *** p < 0.0005; ****p < 0.0001 (vs. VEH), one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons. (c) ENZ at 10 mg/kg reduced liver damage marker, serum ALT(U/L). *p = 0.0298 (10 mg/kg ENZ vs. VEH), one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons. (d) ENZ at 30 mg/kg reduced the number of pGST-positive, preneoplastic foci. Left, Representative photomicrographs (40 × total magnification) of IHC for pGST for VEH (left) and 30 mg/kg ENZ (right) treatment groups. Right, Comparison of the total number of pGST-positive foci between treatment groups. *p = 0.033 (30 mg/kg vs. VEH), one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s Multiple Comparisons. All data represented as mean ± standard deviation.