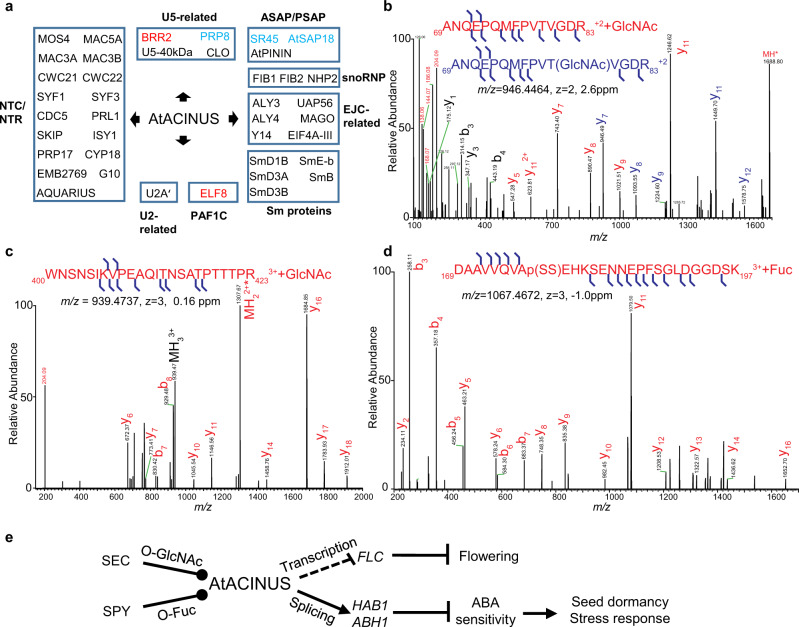
Fig. 7. AtACINUS is O-GlcNAc and O-fucose modified and associates with spliceosomal complexes, transcriptional regulators, and chromatin remodeling proteins.
a Diagram shows functional groups of AtACINUS-associated proteins. Proteins are grouped in boxes based on their association with known complexes or functions. Positive regulators of FLC are highlighted in red and negative regulators in blue. Seven-day-old seedlings were used for the label-free IP-MS experiments and 14-day-old seedlings were used for the 15N stable-isotope-labeling in Arabidopsis (SILIA) quantitative MS experiments. b, c Higher energy collisional dissociation (HCD) mass spectra show O-GlcNAcylation on Thr79 and a sequence spanning amino acid 400–423 of AtACINUS. The sequence ion series that retain this modification (shifted by 203 Da) are labeled in blue (b). The sequence ion series that have lost the modification are labeled in red. HexNAc oxonium ion (m/z 204) and its fragments masses are labeled in red. d HCD spectrum shows O-fucosylation on a sequence spanning amino acid 169–197 of AtACINUS with neutral loss. e Proposed model of a molecular pathway in which nutrient sensing O-GlcNAcylation and O-fucosylation modulate the evolutionarily conserved RSB-domain protein AtACINUS, which controls transcription and alternative RNA splicing of specific target genes to modulate stress hormone sensitivity and developmental transitions such as seed germination and flowering in plants.