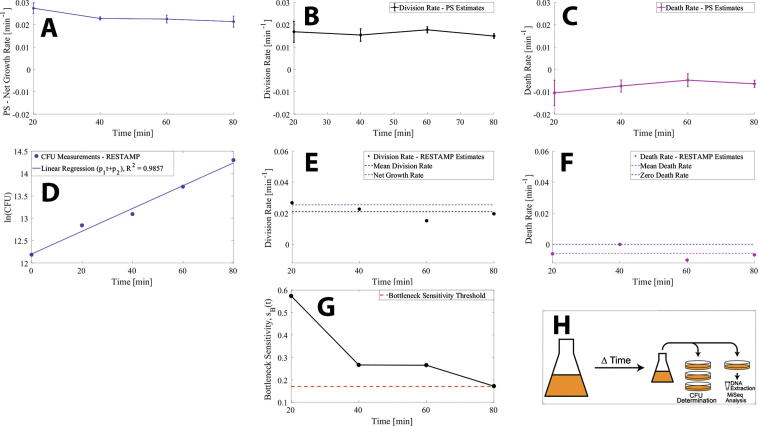
Fig. 5.
Estimated division rates and death rates for RESTAMP and PS for cells growing in LB media. (A) Net growth rate estimates at each time point for three repetitions of a plasmid segregation experiment. The diamonds and bars show the standard error of the mean. (B) Estimates of average division rates using the plasmid segregation method (diamonds) where the bars show the standard error of the mean. (C) Estimates of average death rates using the plasmid segregation method (diamonds) where the bars show the standard error of the mean. (D) A linear regression of the natural logarithm of the CFUs versus time. The slope p1 is the average net growth rate with the 95% confidence interval given in parenthesis where p1 = 0.02547 (0.01984, 0.03111) min−1 and p2 = 12.2 (11.93, 12.48) min−1. (E) Estimated division rates using the RESTAMP method at each time point of the experiment (black circles). The black dashed line is the average division rate and the blue dashed line is the net growth rate. (F) Estimated death rates using the RESTAMP method (magenta circles). The dashed magenta line is the average estimated death rate and the blue line is a death rate of 0. (G) The bottleneck sensitivity (y-axis, black solid line)) for sequencing was calculated according to equation (8) where r = β = 0.025 min−1, t={20, 40, 60, 80} min, N(0) = 1.95 × 105 CFU/ml and NB is the mean sample size on the sequencing chip (S2) where <S2> = {8.643 × 105, 1.16 × 106, 9.4751 × 105, 1.3145 × 106}. The red dashed line corresponds to the bottleneck sensitivity threshold, 0.17. (H) A simple schematic of the experiment also illustrated in Fig. 1C. Samples were taken from an Erlenmeyer flask, which contains either a population of cells with a sequence tag (STAMP) or a population of cells with an identifiable plasmid (PS) in LB media after growing for time t. Colony forming units (CFUs) were determined by serial dilution for all samples in triplicates. For the RESTAMP method, the genomes were extracted and tag frequencies were determined by next-generation sequencing. For the PS method the fraction of cells carrying the conditionally replicative plasmid were determined by selective plating. The experiments were repeated biologically independently three times. Rate estimates for all trials at each time point and experimental CFU and NB values are available for download on SourceForge (see 6 – Code). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)