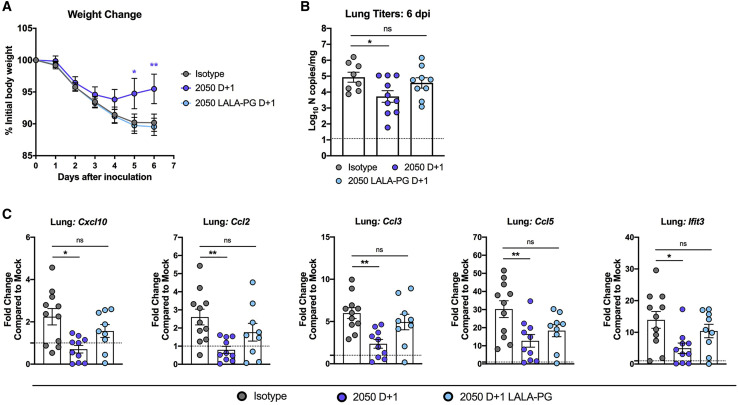
Figure 7.
Fc effector functions enhance the therapeutic activity of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in Syrian hamsters
(A–C) Seven-month-old female Syrian hamsters were inoculated by the intranasal route with 5 × 105 PFU of SARS-CoV-2. At 1 dpi (D+1), hamsters were given 1 mg of COV2-2050 or COV2-2050 LALA-PG by intraperitoneal injection.
(A) Weight change (mean ± SEM; n = 8–10, 2 experiments: two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; comparison to the isotype control mAb-treated group).
(B) Viral RNA levels at 6 dpi in the lung (n = 8–10, 2 experiments: one-way ANOVA with Turkey’s post-test: ns not significant, ∗p < 0.05, comparison to the isotype control mAb-treated group).
(C) Fold change in gene expression of indicated cytokines and chemokines in lung homogenates. Data are normalized to Rpl18 and compared to naive controls (2 experiments, n = 8–10 per group, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01). Dotted lines indicate the mean cytokine or chemokine transcript levels in naive hamsters.