Figure 4.
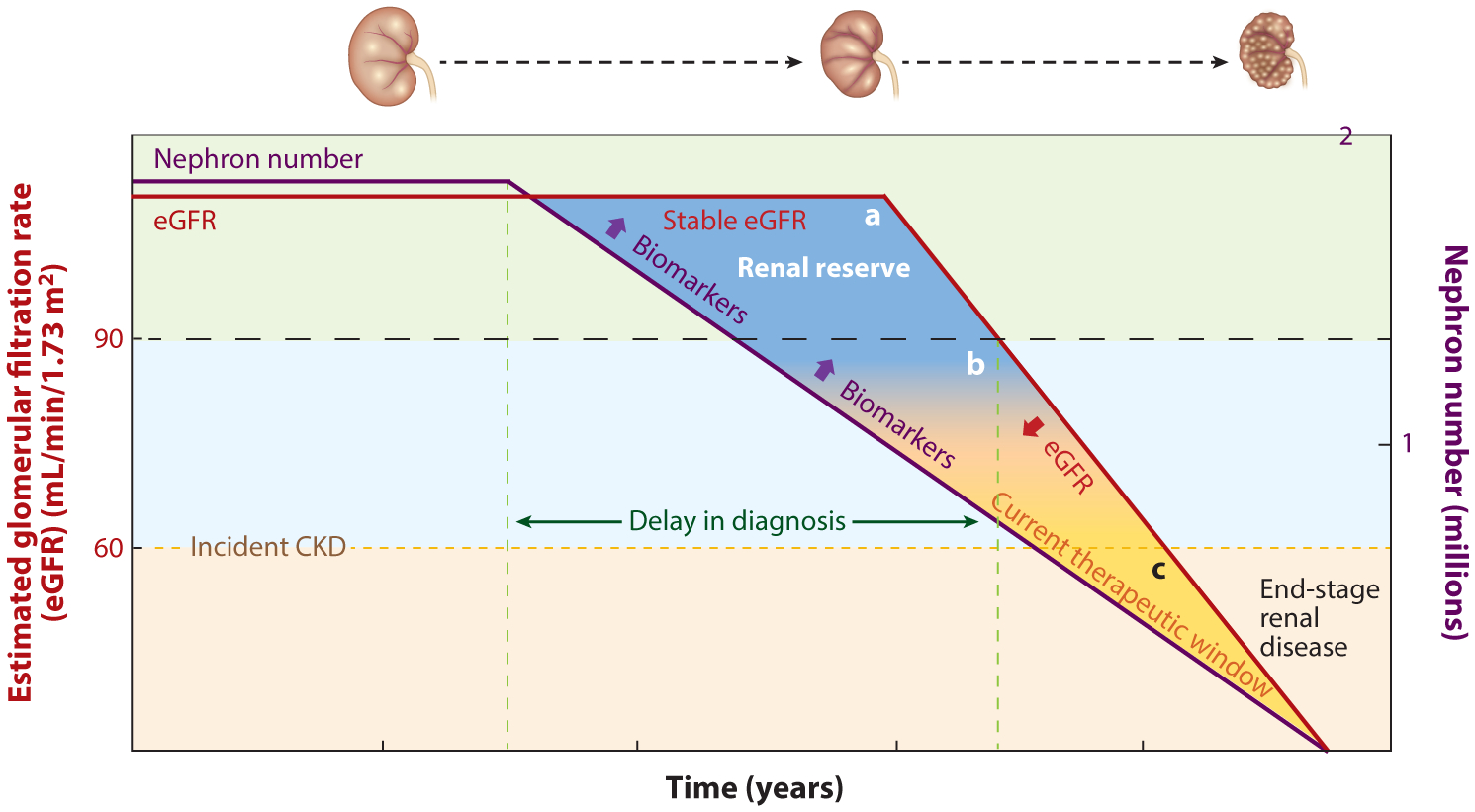
Opportunities for biomarkers of kidney tubular health to advance care in CKD. The left-hand y-axis depicts the eGFR, and the red line represents the eGFR trajectory with respect to time over the disease course. The right-hand y-axis depicts the number of remaining nephrons in millions, and the purple line depicts the nephron number with respect to time over the disease course. The delay in diagnosis (labeled as the distance between the dashed green vertical lines) may be reduced by use of biomarkers of kidney tubular health, which begin to increase as the nephron number begins to fall. In the earliest stages of CKD, the number of nephrons begins to decrease prior to being captured by clinically meaningful decreases in eGFR, as the kidney is able to compensate for loss of nephrons via the phenomenon of renal filtration reserve. Trapezoid A is labeled as renal reserve and encompasses the early course of disease when nephron numbers have begun to fall, yet eGFR is stable or only beginning to decline but is still above the threshold for clinical classification of CKD (dashed black horizontal line at eGFR of 90 mL/min/1.73 m2). In this range, novel biomarkers may address the critical limitations of serum creatinine and eGFR by detecting the earliest stages of kidney damage of incident CKD. Trapezoid B encompasses a region in which the effects of renal reserve may persist but are tapering out. In this range, decreases in nephron number may be paralleled by decreases in eGFR; thus, while biomarkers may be increasing and signaling intrinsic kidney damage, the kidney may also manifest loss of nephron number as commensurate eGFR declines because of the loss of renal reserve at this point. Thus, biomarkers may have less utility at this stage in the progression of CKD in discerning injury to the kidney; however, they may be able to address other limitations of serum creatinine. Triangle C represents advanced stages of CKD, in which the current therapeutic window for intervention lies. Utilizing biomarkers of tubular injury may allow for identification of therapeutic targets and shift this window to earlier points in the disease course. Abbreviations: CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.
