Figure 1.
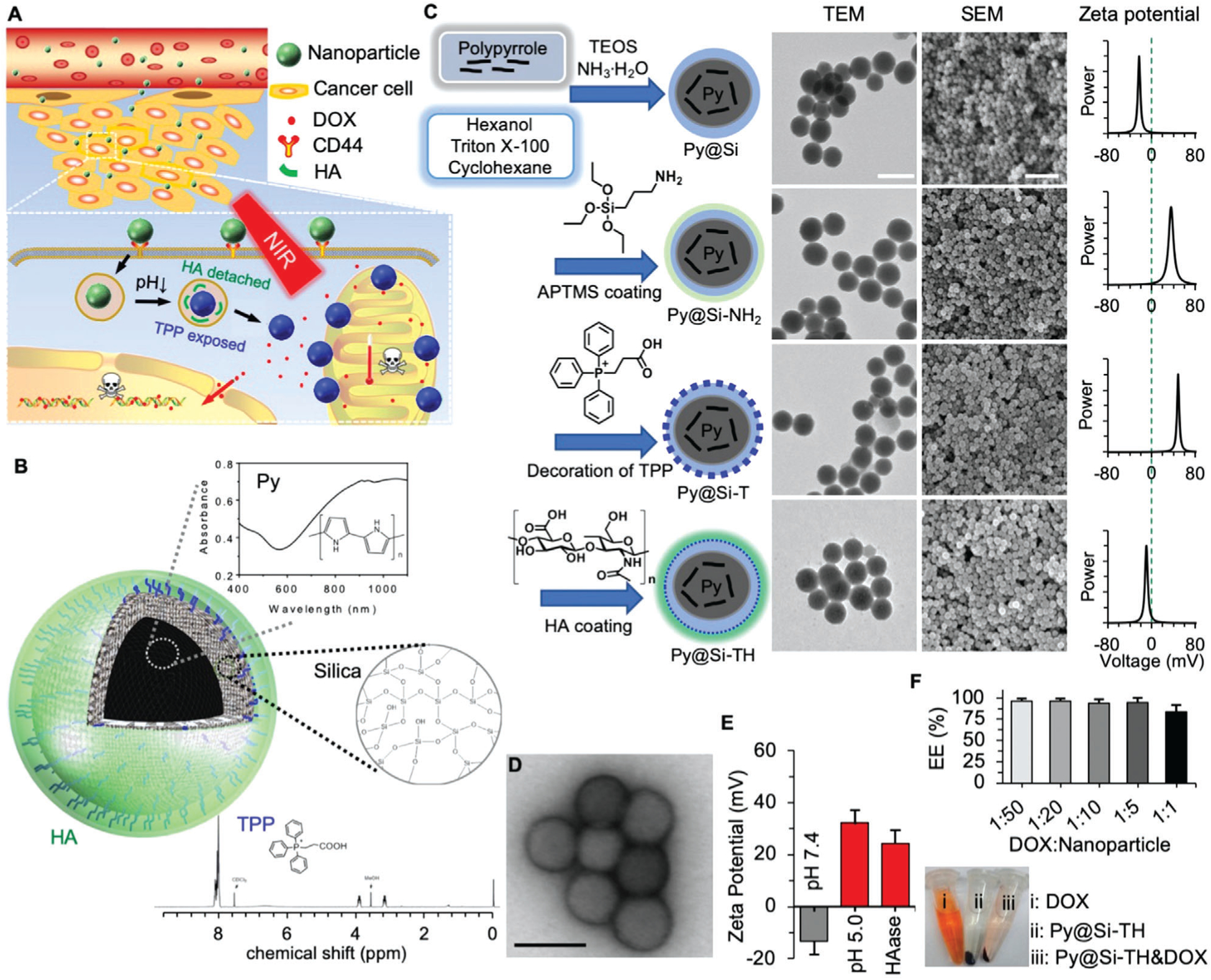
Synthesis and characterization of nanoparticles. A) A schematic illustration of the nanoparticle in targeting tumor via the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect of tumor vasculature, cancer cells via CD44, and mitochondria via triphenylphosphonium (TPP) for chemo-photothermal therapy of cancer. B) A schematic illustration of the structure of the nanoparticle together with materials in the nanoparticles. Py: polypyrrole. HA: hyaluronic acid. C) The procedure for preparing Py-embedded silica (Py@Si) nanoparticles, modifying the Py@Si nanoparticles with (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane (APTMS) to form Py@Si-NH2 nanoparticles, coating the Py@Si-NH2 nanoparticles with TPP to produce mitochondria-targeting Py@Si-T nanoparticles, and finally, coating the Py@Si-T nanoparticles with HA to produce Py@Si-TH nanoparticles. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were also given to show the morphology of the nanoparticles. The difference in surface zeta potential of the Py@Si, Py@Si-NH2, Py@Si-T, and Py@Si-TH nanoparticles demonstrating the successful sequential modification of the positively charged APTMS and TPP and negatively charged HA on the nanoparticle surface. Scale bar: 100 and 500 nm for the TEM and SEM images, respectively. D) TEM images of Py@Si-TH nanoparticles with negative staining showing the HA coating on the outermost surface of the nanoparticles. Scale bar: 100 nm). E) Zeta potential data showing HA detachment from Py@Si-TH nanoparticles after treatment at low pH or with hyaluronidase (HAase). All the zeta potential data were measured by redispersing the nanoparticles in deionized water at neutral pH after the treatments. F) Encapsulation efficiency (EE) of doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) by simply mixing it with Py@Si-TH nanoparticles at different feeding ratios (DOX:nanoparticle in weight) for 1 h. Centrifuge tubes depicting the color of DOX, Py@Si-TH nanoparticles, and mixture of DOX and Py@Si-TH nanoparticles (1:1) after centrifuging (13 000 × g), indicating the high EE of DOX with the nanoparticles at the high feeding ratio.
