Figure 5 |. Epithelial DUOX2 and TLR4-shaped microbiota induce tumor initiation.
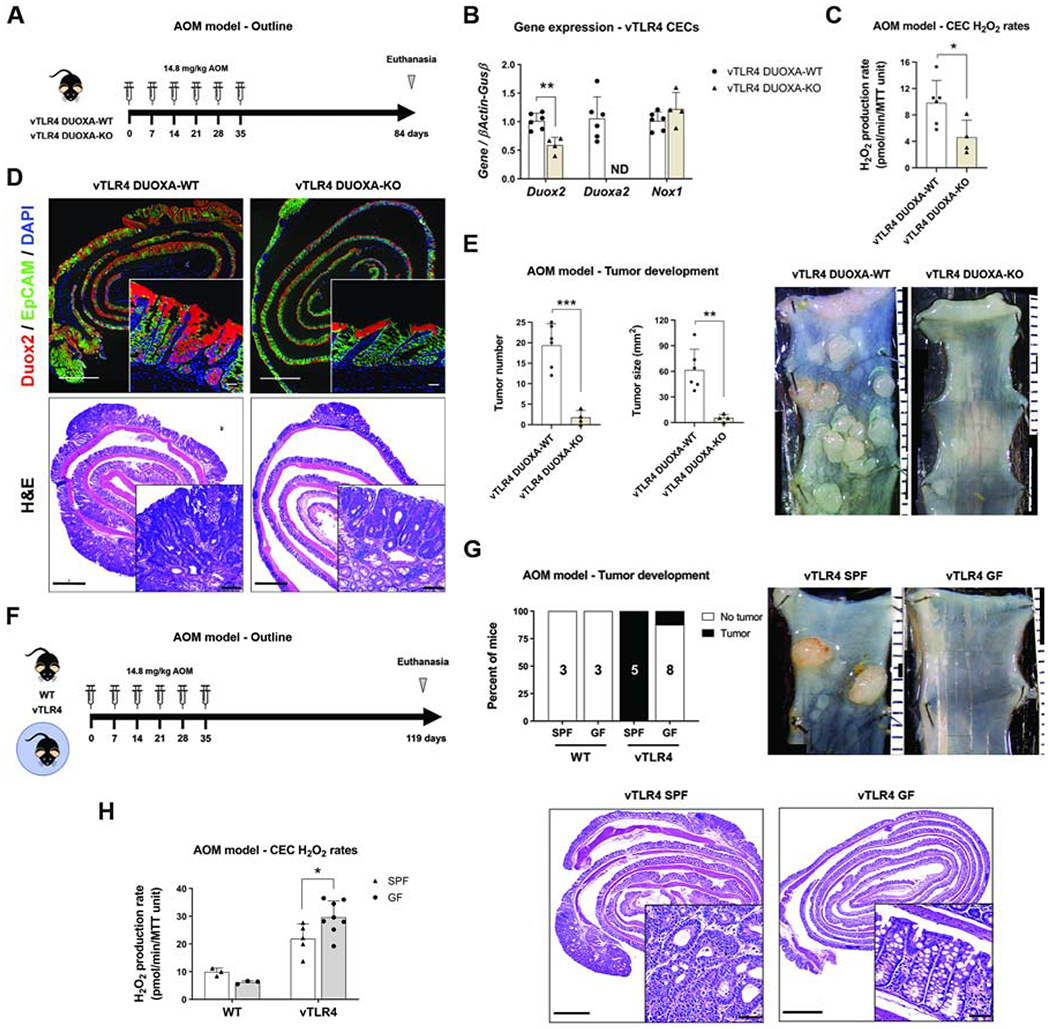
(A) Villin-TLR4 DUOXA-KO and their villin-TLR4 littermates underwent the AOM model of CRC for 12 weeks. (B) Gene expression in CECs. Deletion of Duoxa (non-detectable, ND) caused a significant downregulation of Duox2 (**P<0.01; n=4-6 mice). (C) CEC production of H2O2 in villin-TLR4 mice was reduced by deletion of DUOXA (*P<0.05; n=4-6 mice). (D) Representative micrographs of Duox2 in situ hybridization and H&E for AOM-treated villin-TLR4 mice. Micrograph scale bar = 1 mm; inset scale bar = 25 and 50 μm, respectively. (E) Tumor number (***P<0.001) and size (**P<0.01) were decreased in villin-TLR4 lacking DUOXA (n=4-6 mice). Micrographs show representative distal colons of each group of mice; scale bar in mm. (F) Villin-TLR4 mice and their WT littermates raised in SPF and GF conditions underwent the AOM model of CRC for 17 weeks. (G) Percentage of mice developing tumors in each condition is shown in black (n=3-8 mice). Tumor development was compared between groups by Chi-square test. Representative micrographs of AOM-treated villin-TLR4 mice grown in SPF and GF conditions. Micrograph scale bar = 1 mm; inset scale bar = 50 μm. (H) Epithelial H2O2 production rate at the time of euthanasia (n=3-8 mice). Villin-TLR4-SPF vs villin-TLR4-GF, *P<0.05, as determined by two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s post-hoc test.
