Fig. 3. Increased systemic GPLD1 ameliorates impaired neurogenesis and cognition in the aged hippocampus.
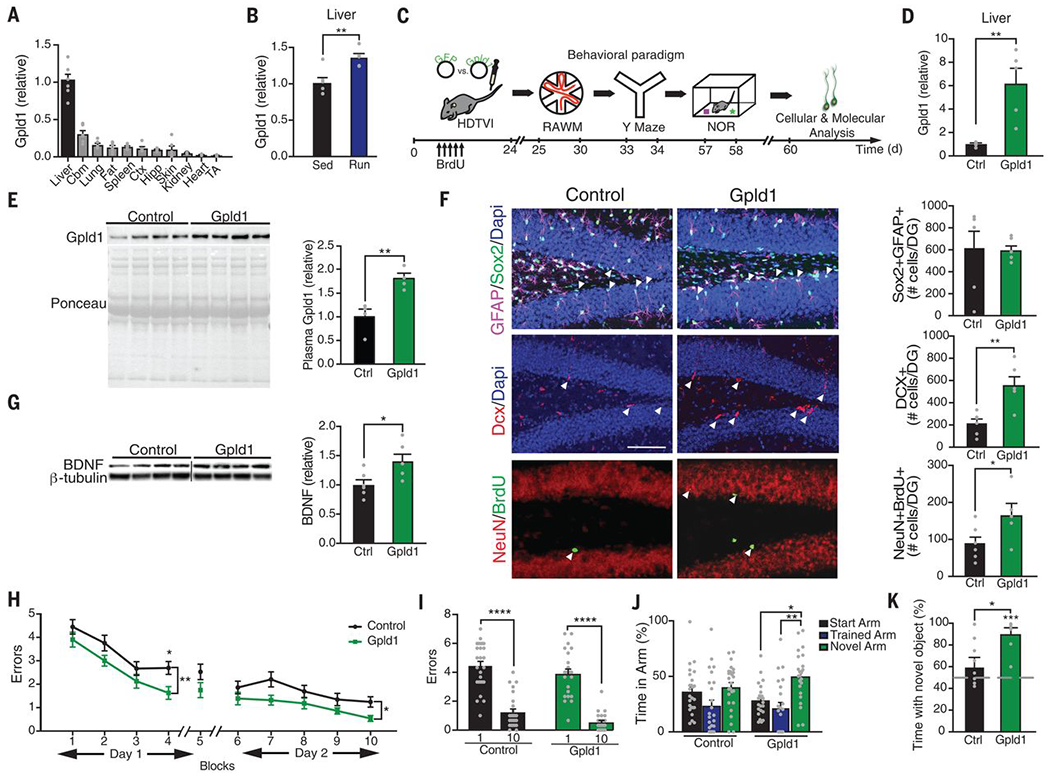
(A and B) Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of Gpld1 across tissues in sedentary aged mice (A) and in liver of exercised and sedentary aged mice (B). Gene expression is measured relative to Gapdh (n = 5 or 6 per group). Abbreviations: Cbm, cerebellum; Ctx, cortex; Hipp, hippocampus; TA, tibialis anterior muscle. (C) Aged (18 months) mice were given HDTVI of expression constructs encoding either Gpld1 or GFP control. Schematic illustrates chronological order of HDTVI, cognitive testing, and cellular and molecular analysis. (D) qRT-PCR of Gpld1 in liver of aged mice expressing Gpld1 or GFP control. Gene expression is measured relative to Gapdh (n = 5 per group). (E) Western blot with corresponding Ponceau S stain and quantification of Gpld1 in equal volumes of blood plasma from individual aged mice expressing Gpld1 or GFP control (n = 4 per group). (F) Representative microscopic fields and quantification of GFAP/Sox2 double-positive, Dcx-positive, and NeuN/BrdU double-positive cells in the DG of the hippocampus of aged mice expressing Gpld1 or GFP control (n = 6 per group; arrowheads point to individual cells; scale bar, 100 μm). (G) Western blot and quantification of BDNF in the hippocampus of aged mice expressing Gpld1 or GFP control (n = 6 per group). Quantification is normalized to β-tubulin. (H and I) Spatial learning and memory were assessed by RAWM as number of entry errors committed during the training and testing phases. Overall learning and memory was analyzed between block 1 and block 10 (1 block = 3 trials; n = 26 per group). (J) Spatial working memory was assessed by YMaze as time spent in the start, trained, and novel arms during the testing phase (n = 23 to 25 per group). (K) Object recognition memory was assessed by NOR as time spent exploring a novel object 24 hours after training (n = 8 to 12 per group). Data are means ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 [t test in (B), (D), (E), (F), (G), and (K); repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test in (H); ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test in (I) and (J); one-sample t test versus 50% in (K)].
