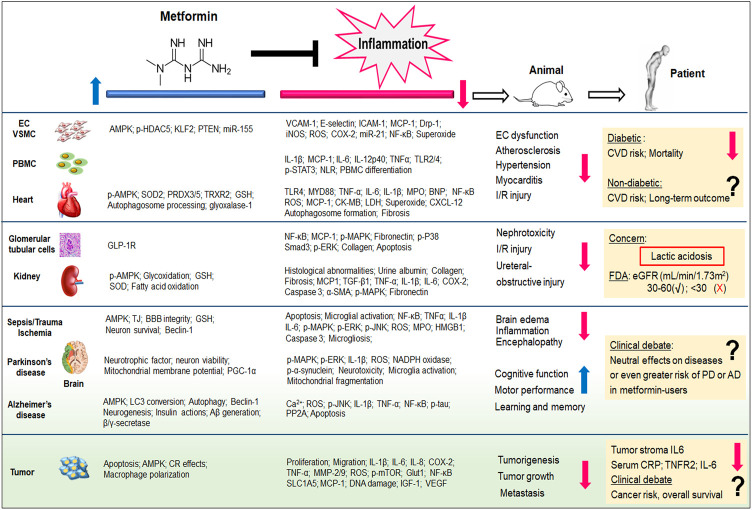
FIGURE 1.
Metformin exhibits potent inflammation-inhibitory effects, irrespective of its capability of glucose control. Both pre-clinical (from cells and animal models) and clinical (from patients) evidence demonstrate the therapeutic potentials of metformin to cardiovascular diseases, kidney diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, as well as cancer. The pleiotropic actions of metformin and its anti-inflammatory properties have been reviewed in this article. Aβ, amyloid beta; AD, alzheimer’s disease; BBB, blood-brain barrier; BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; CK-MB, creatinine kinase-myocardial band; COX, cyclooxygenase; CR, calorie restriction; CRP, C-reactive protein; CVD, cardiovascular diseases; CXCL12, C-X-C motif chemokines ligand 12; Drp-1, dynamin-related protein-1; EC, endothelial cell; ERK, extracellular-signal regulated kinases; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; GLP-1R, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; Glut1, Glucose transporter 1; GSH, glutathione; HDAC5, histone deacetylase 5; HMGB1, high mobility group box; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; KLF2, kruppel-like factor 2; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; miR, microRNA; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MPO, myeloperoxidase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; MYD88, myeloid differentiation protein 88; NLR, Neutrophil-Lymphocyte ratio; p, phosphorylation; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PD, Parkinson’s disease; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; PGF2α, prostaglandin F2α; PRDX, peroxiredoxin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Smad3, SMAD family member 3; SLC1A5, solute-carrier family 1 member 5; SOD2, superoxide dismutase 2; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; TJ, tight junction; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRXR, thioredoxin reductase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell. The blue arrow indicates the up-regulatory effects of metformin, whereas the red arrow indicates metformin’s down-regulatory effects.