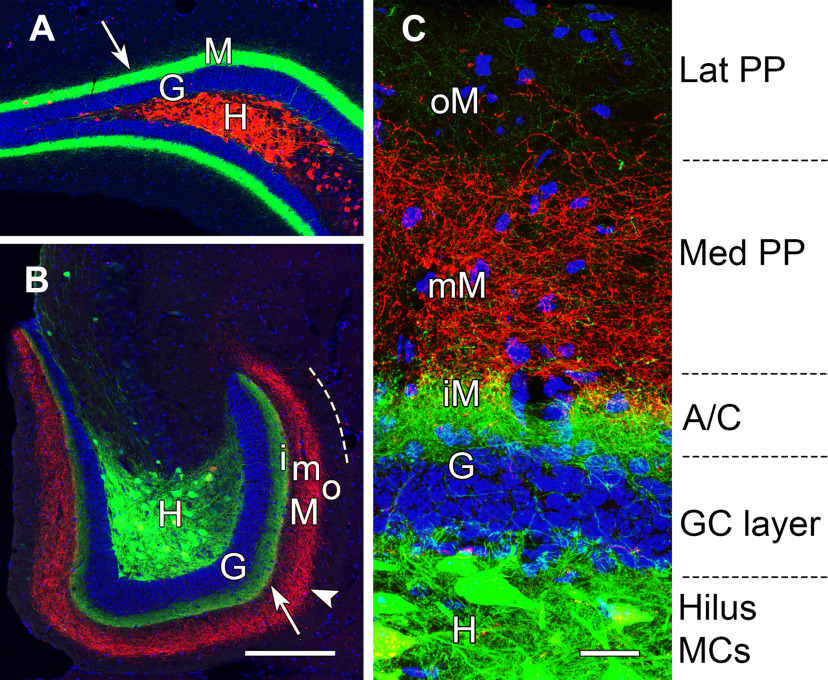
Figure 8.
MCs in the dorsal and ventral DG form distinct laminar projections to the molecular layer. A, B, Axonal projections from ventral MCs (eYFP) in the hilus (H) form dense projections (arrows) to the inner molecular layer (M), adjacent to the DAPI-labeled nuclei of granule cells (G), throughout the longitudinal extent of the DG. These projections are strongest at dorsal levels (A), distant from their cell bodies of origin. In contrast, dorsal MCs (mCherry) form projections that differ in their locations at dorsal and ventral locations. While these projections overlap with those of ventral MCs at dorsal levels, they assume non-overlapping laminar distributions (arrowhead) at caudal levels (B) and are located in the middle molecular layer (mM), between the axonal projection of ventral MCs in the inner molecular layer (iM) and the unlabeled outer molecular layer (oM). Dashed line in B indicates the outer border of the molecular layer. C, At higher magnification, the laminar pattern can be related to the expected innervation from associational/commissural (A/C) fibers of MCs, medial perforant path (PP), and lateral PP. Scale bars: 200 µm (A, B) and 25 µm (C).