Figure 1.
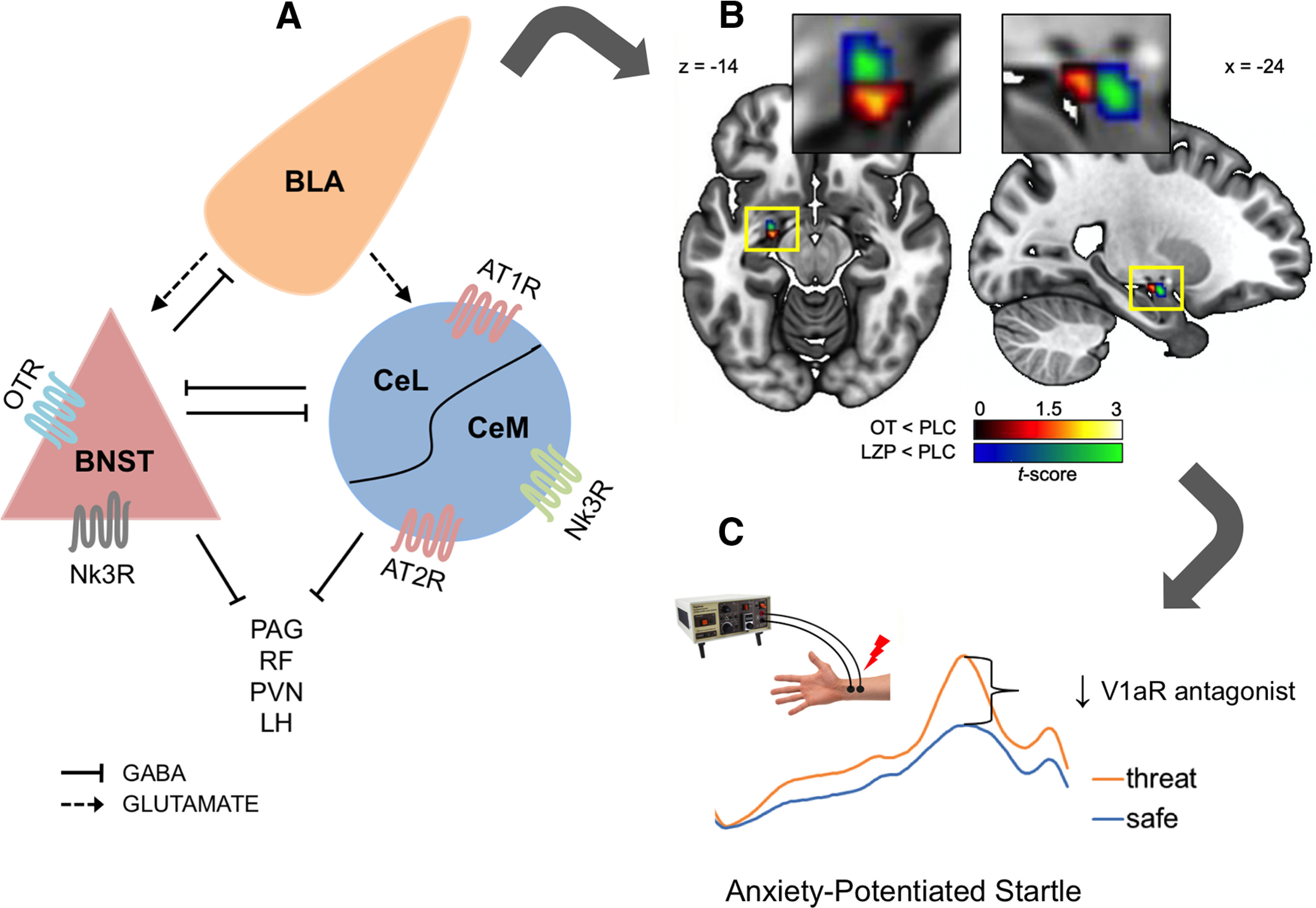
Limbic neuropeptides and their receptors are promising targets for PTSD prevention and treatment. Translational potential of the limbic neuropeptides is illustrated by gray arrows from preclinical studies using animals models of fear and anxiety (A), to neuroimaging studies on the effects of the neuropeptides (e.g., oxytocin) on the amygdala activity in humans (B), to behavioral studies (anxiety-potentiated startle) testing the effects of compounds targeting neuropeptidergic receptors (e.g., vasopressin receptor antagonist) on anxiety measured in humans (C). A, Neuropeptidergic GPCRs in the extended amygdala modulate unique phases of fear learning and thereby can moderate core features of PTSD pathophysiology. OTRs in rat BNST facilitate fear discrimination by strengthening fear responses to predictable, signaled threats. Nk3R-expressing cells in the BNST mediate trauma-induced aggression in mice, whereas in mouse CeM, the Nk3R antagonist osanetant prevents fear memory consolidation. In the CeL and CeM, AT1R antagonist accelerates fear memory extinction in mice. LH, Lateral hypothalamus; PAG, periaqueductal gray; RF, reticular formation. Solid lines indicate inhibitory (GABAergic) projections. Dashed arrows indicate excitatory (glutamatergic) projections. B, Using 7T fMRI in healthy human subjects, it was shown that, compared with placebo (PLC), oxytocin (OT, 24 IU) dampened the left centromedial amygdala response to fearful relative to neutral faces in a manner similar to lorazepam (LZP, 1 mg) (red-yellow cluster represents OT vs PLC; blue-green cluster represents LZP vs PLC). C, A novel V1aR antagonist, SRX246, decreases startle amplitude during presentation of an unpredictable threat (mild electrical shock) in a translational paradigm of anxiety in humans. Traces represent processed EMG recordings of eye blink startle after administration of a loud white noise. In the safe condition, participants are not at risk of shock. In the unpredictable threat condition, participants can receive a mild electric shock (red lightning bolt) at any time. Anxiety-potentiated startle is quantified as the change in startle amplitude from safe to threat.
