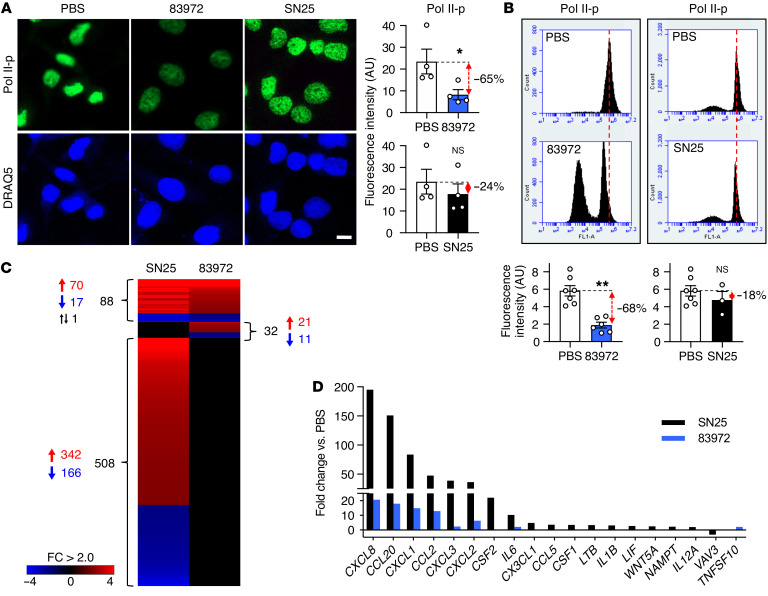
Figure 1. Bacterial inhibition of Pol II phosphorylation.
(A and B) Identification of E. coli SN25 as a loss-of-function mutant. Pol II Ser2 phosphorylation was quantified in human kidney cells infected with the ABU strain E. coli 83972 or E. coli SN25, a re-isolate from a human carrier of E. coli 83972. (A) Confocal microscopy and (B) flow cytometry. Nuclei were counterstained with DRAQ5. Histograms show quantification of fluorescence intensity. Scale bar: 10 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–6 experiments). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with PBS control by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple-comparison test. (C and D) Comparative gene expression analysis of host cells infected with E. coli 83972 or SN25. (C) Heatmap: >500 genes were regulated exclusively in response to E. coli SN25. (D) E. coli SN25 activated innate immune response genes more efficiently than E. coli 83972. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments; fold change (FC) > 2.0 compared with PBS control.