Fig. 1.
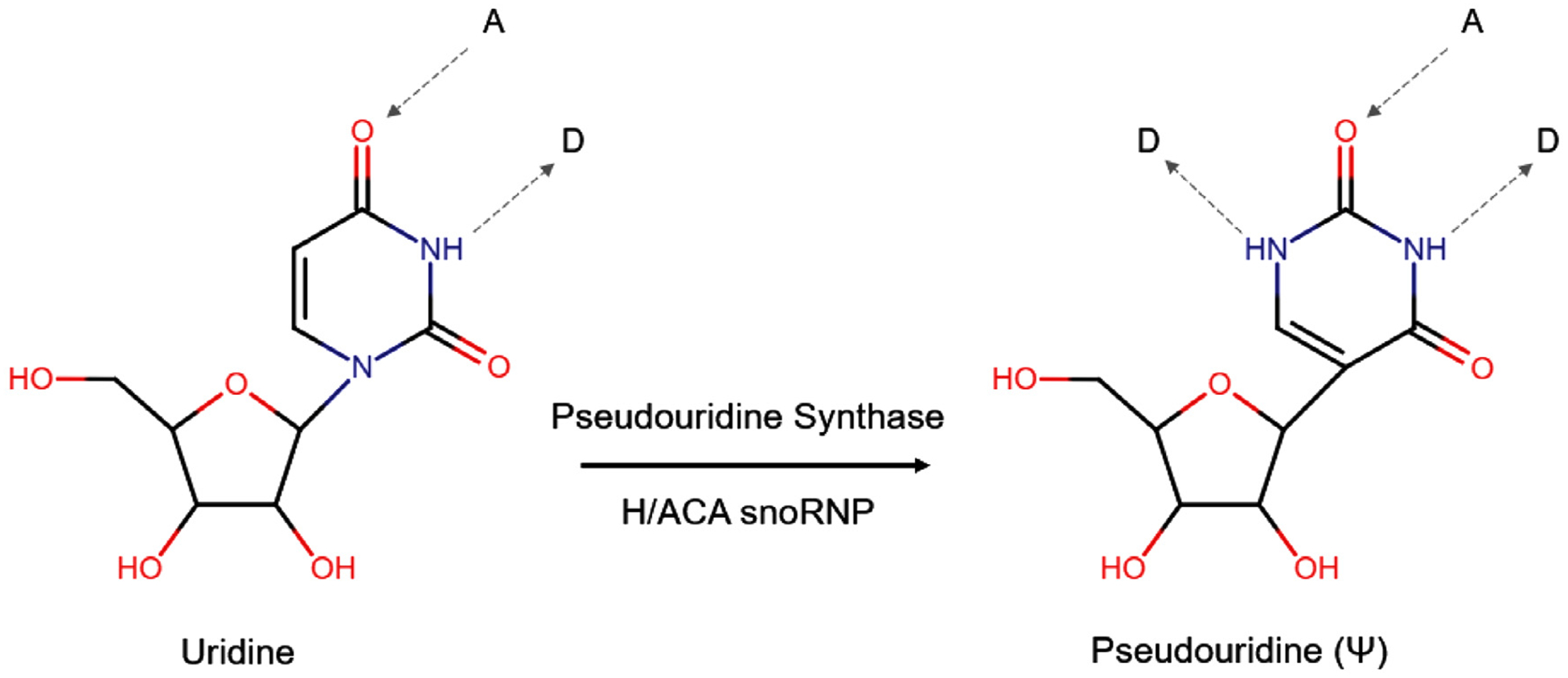
Biosynthesis and chemical properties of pseudouridine. The isomerization of uridine to pseudouridine is performed by either standalone pseudouridine synthases (PUSs) or H/ACA snoRNP complexes containing the catalytic component dyskerin (DKC1), additional core proteins (NOP10, GAR1 and NHP2) and an H/ACA snoRNA which serves as a guide. Uridine can accept (A) and donate (D) one hydrogen bond (gray dashed arrow) each whereas pseudouridine can donate an additional hydrogen bond.
