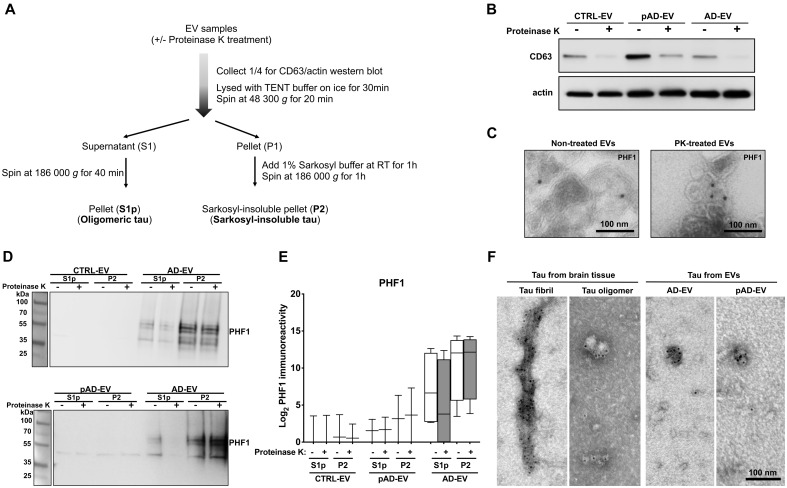
Figure 2.
PK treatment of human brain derived EVs for biochemical characterization. (A) Workflow of the tau purification by sequential centrifugation after with or without PK treatment. (B) Western blot analysis of non-treated and PK-treated EVs from three groups (CTRL, pAD and Alzheimer’s disease) with CD63 and actin antibodies. (C) Immunoelectron microscopy images of ultrathin-sectioned Alzheimer’s disease EVs for PHF1+ tau with or without PK-treatment. Images were captured at direct magnification ×30 000, with the 10 nm immunogold labelling. (D) Western blot analysis of oligomer-enriched (S1p) and sarkosyl-insoluble tau-enriched (P2) fractions from EVs for PHF1 with or without PK-treatment. (E) Semi-quantification of PHF1 immunoreactivity. Two donors per group for CTRL and pAD and four donors for the Alzheimer’s disease group. (F) Immunoelectron microscopy of isolated tau fibrils, oligomers or sarkosyl-insoluble fraction of EVs from human Alzheimer’s disease brain tissue. Images were captured by TEM at direct magnification ×40 000, with the 5-nm immunogold labelling for PHF1. (A–F) Donors 1 and 2 (control, CTRL), 4 and 5 (pAD), and 7–10 (Alzheimer’s disease, AD) were used (Supplementary Table 2).